designing with metals ceramics polymers and composites

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 2 doc
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... chapter 11 for the case of metals and ceramics, and in chapter for polymers Plastic deformation allows to form components or semi-finished parts during manufacturing, with processes like rolling, ... unusual to work with E, G, and ν Instead, the components S11 , S12 , and S44 of the compliance matrix or C11 , C12 , and C44 of the elasticity matrix are used 12 13 Directions and planes in crystals ... a number and unoccupied spaces mark zero values The upper right and lower left sub-matrices describe the relation between shear stresses and normal strains and between normal stresses and shear...
- 40
- 348
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 4 docx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... the notch root d, the notch depth t (with 2t = D − d), and the notch radius As an example, consider a shaft with D = 100 mm and a notch with radius = mm and depth t = mm (a semi-circular notch) ... calculation of the critical crack length with equation (5.28), the yield strength Rp was used for metals and polymers and the compressive strength Rcm for ceramics The geometry factor Y was taken ... toughness and crack sensitivity of some materials The latter is quantified by the critical crack length ac for Y = [8, 11, 21, 27] Here, Rp is used for metals and polymers and Rcm for ceramics...
- 40
- 416
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 5 doc
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... between ∆a and JR is almost linear With increasing load, the cavities coalesce with each other and the crack, causing a ‘true’ growth of the crack (subfigure ○) This is called crack initiation and occurs ... material is loaded at high temperatures, the crack can grow In metals and ceramics, pores are frequently responsible for this because they form and coalesce in the highly-stressed region in front of ... sharp-edged with a small radius of curvature, and this is ensured by creating it through cyclic loading The quantities G, H, B, W , and s from figure 5.14(b) must, according to the standard astm...
- 40
- 284
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 6 ppt
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... therefore increase with increasing ; this is more pronounced in body-centred cubic metals This agrees with experimental observation (see gure 6.29)
6 Mechanical behaviour of metals ắIII ắII ... relevant, the vacancy density and mobility within the crystal must be large As explained in appendix C.1, the vacancy density and mobility increase exponentially with the temperature Therefore, ... important way of strengthening metals is to alloy them with elements that are dissolved in the crystal lattice and form a solid solution Such atoms 204 Mechanical behaviour of metals (a) Substitutional...
- 40
- 356
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 7 pptx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... parts 7.5 Strengthening ceramics Similar to metals, strengthening ceramics is of great technical importance The methods used for metals (section 6.4) cannot be used for ceramics because they are ... decompose before 8.2 Time-dependent deformation of polymers Young’s modulus of polymers is about two orders of magnitude smaller than that of metals and ceramics (see table 2.1), whereas the yield strength ... viscoplasticity) can also occur in metals and ceramics at high temperatures and will be discussed in chapter 11
¾/MPa 12 25 10 20 15 23 °C 40 °C 60 °C Mechanical behaviour of polymers 80 °C 266 40 30...
- 40
- 306
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 8 pot
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... dependence of Young’s modulus of a copolymer Alternating and random copolymers have a glass temperature between both basic polymers; graft and block copolymers behave like semi-crystalline thermoplastics ... bands, created at an angle between 45° and 60° [44, 82, 132] to the loading direction (figure 8.16) Formation of shear bands is especially important under compressive loads Within the shear bands, ... made of protein fibres, spun to strings with a diameter between about µm and 10 µm in spider silk and 10 µm and 50 µm in silk of the silk moth Proteins are polymers comprising amino acids as monomers...
- 40
- 323
- 0
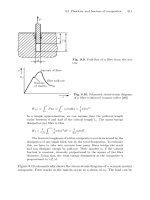
Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 9 pot
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... Examples of composites 9.4.1 Polymer matrix composites Polymers are well-suited as matrix materials due to their low density and their low processing temperatures Accordingly, composites with a polymer ... industry and many other areas, for example in sports equipment Polymer matrix composites can be used with long and short fibres We will start this section by discussing long-fibre polymer matrix composites ... are polyester and epoxy resins Thermoplastic matrix materials are polyethylene (pe) and polypropylene (pp), but the use of thermoplastics with aromatic rings on the chain and thus with increased...
- 40
- 291
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 10 pptx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... silicon carbide, and a psz ceramic [6, 38, 53, 57, 87] reduced by cyclic loading The fatigue-crack-growth threshold ∆Kth is almost the same in ceramics and metals Nevertheless, metals have one ... large effect on the number of cycles This phenomenon is restricted to metals and polymers and will be discussed for the case of metals in the next section If the maximum stress σmax reaches the strength ... intensity factor ∆K = ∆σ πa Y and on the R ratio According to this, a short crack loaded with a large stress range will propagate with the same rate as a long crack loaded with a small stress range...
- 40
- 409
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 11 pptx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... and a weight loading the band with a force FB = const The cross section of both rubber bands is identical (A) Assume that both rubber bands are linear-elastic Young’s modulus of the rubber band ... The rubber band is elon- (b) Booth B The rubber band is loaded gated by the same distance ∆lA always with the same force FB always Fig 12.1 Candy catapults, shown in the loaded state and calculating ... element can be described with the equation σ = Eε, with σ being the stress, ε the strain, and E Young’s modulus A dashpot element behaves according to ε = σ/η, with strain rate ε and viscosity η ˙ ˙...
- 40
- 304
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 12 potx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... averaged over fibre and matrix and will not occur at any point in the component Af /A and Am /A are the area fractions of fibre and matrix and thus equal the volume fractions ff and fm because the ... divided into two parts, one for the fibre and one for the matrix: F = Ff + Fm If we call the total cross section A and the cross section of fibre and matrix Af and Am , respectively, we find for the ... stress Thus, we find C = σ and » „ «– σ E ε= − exp − t E η The strain increases with time and approaches a value σ/E because the dashpot element will have relaxed completely and all of the stress...
- 40
- 350
- 0

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 13 docx
Ngày tải lên :
11/08/2014, 15:20
... Microstructure, Processing and Design Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1986 10 N W Ashcroft and N D Mermin: Solid State Physics itps Thomson Learning, 2000 11 D R Askeland and P P Phleé: The Science and Engineering ... Clegg and G D Paterson: Ductile particle toughening of hydroxyapatite ceramics using platinum particles In A Atrens, J N Boland, R Clegg, and J R Griffiths (editors): Structural Integrity and Fracture, ... ceramic design and process engineering In S J Schneider (editor): Ceramics and Glasses, volume of Engineered Materials Handbook, pages 29–37 asm International, 1991 92 J Lemaitre (editor): Handbook...
- 40
- 308
- 0

mechanical properties of polymers and composites nielsen doc
Ngày tải lên :
22/03/2014, 12:20
... properties of polymers and composites / Lawrence E Nielsen Robert F Landel — 2nd ed., rev and expanded p cm — (Mechanical engineering ; 90) Includes bibliographical references and index ISBN ... and folding which are possible within and between lamellae and between ribbon surfaces In real, well-crystallized polymers, these variations he relatively far apart and the forms SC" CF, SB and ... of thermal expansion Ribbon-Filled Composites Other Types of Composites A Flake-filled polymers B Composites with thick interlayers C Interpenetrating network composites Summary Problems References...
- 138
- 878
- 0

mechanical properties of polymers and composites nielsen pot
Ngày tải lên :
22/03/2014, 13:20
... properties of polymers and composites / Lawrence E Nielsen Robert F Landel — 2nd ed., rev and expanded p cm — (Mechanical engineering ; 90) Includes bibliographical references and index ISBN ... and folding which are possible within and between lamellae and between ribbon surfaces In real, well-crystallized polymers, these variations he relatively far apart and the forms SC" CF, SB and ... of thermal expansion Ribbon-Filled Composites Other Types of Composites A Flake-filled polymers B Composites with thick interlayers C Interpenetrating network composites Summary Problems References...
- 138
- 438
- 0

MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS AND COMPOSITES pot
Ngày tải lên :
26/06/2014, 23:20
... properties of polymers and composites / Lawrence E Nielsen Robert F Landel — 2nd ed., rev and expanded p cm — (Mechanical engineering ; 90) Includes bibliographical references and index ISBN ... and folding which are possible within and between lamellae and between ribbon surfaces In real, well-crystallized polymers, these variations he relatively far apart and the forms SC" CF, SB and ... of thermal expansion Ribbon-Filled Composites Other Types of Composites A Flake-filled polymers B Composites with thick interlayers C Interpenetrating network composites Summary Problems References...
- 138
- 413
- 1

Nielsen. Lawrence E. Mechanical properties of polymers and composites nielsen doc
Ngày tải lên :
27/06/2014, 17:20
... properties of polymers and composites / Lawrence E Nielsen Robert F Landel — 2nd ed., rev and expanded p cm — (Mechanical engineering ; 90) Includes bibliographical references and index ISBN ... and folding which are possible within and between lamellae and between ribbon surfaces In real, well-crystallized polymers, these variations he relatively far apart and the forms SC" CF, SB and ... of thermal expansion Ribbon-Filled Composites Other Types of Composites A Flake-filled polymers B Composites with thick interlayers C Interpenetrating network composites Summary Problems References...
- 138
- 401
- 0

Mechanical properties of polymers and composites-Nielsen Episode 1 doc
Ngày tải lên :
13/08/2014, 16:21
... properties of polymers and composites / Lawrence E Nielsen Robert F Landel — 2nd ed., rev and expanded p cm — (Mechanical engineering ; 90) Includes bibliographical references and index ISBN ... STATES OF AMERICA MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS AND COMPOSITES SECOND EDITION,REVISED AND EXPANDED LAWRENCE E.NIELSEN Monsanto Company St Louis Missouri F LANDEL Jet Propulsion Laboratory California ... of thermal expansion Ribbon-Filled Composites Other Types of Composites A Flake-filled polymers B Composites with thick interlayers C Interpenetrating network composites Summary Problems References...
- 10
- 382
- 1

Mechanical properties of polymers and composites-Nielsen Episode 2 pot
Ngày tải lên :
13/08/2014, 16:21
... strain, a modulus that decreases with time is obtained Stress-relaxation experiments are very important for a theoretical understanding of viscoelastic materials With experimentalists, however, ... constant rate, and such tests are becoming commonplace with the advent of commercially available loadcontrolled test machines Stress-strain tests have traditionally been the most popular and universally ... been the most popular and universally used of alt mechanical tests and are described by ASTM standard Vests such as D638, D882, and D412 These tests can be more difficult to interpret than many...
- 10
- 314
- 0

Mechanical properties of polymers and composites-Nielsen Episode 3 potx
Ngày tải lên :
13/08/2014, 16:21
... by the pairs of polymers polypropylene ( T g = C) and polyisobutylene (Tg = -70 C), and poly(vinyi chloride) (Tg=87 C) and poly(vinylidene chloride) (Tg =- 19°C) The symmetrical polymers have lower ... important role (54) in unsymmetrical polymers Thus syndiotactic and isoitactic poly( methyl methacrylate) have Tg values of 115 and 45 C respectively T h e flexibility and cohesive energy density or ... Kreibich and Bauer (61) have amended and extended this expression and shown that the constant can be related to E(coh) |cf equation (31) | DiMarzjo (93), Nielsen (88), DiBenedetto (94), and others...
- 10
- 301
- 0
Tìm thêm:
- hệ việt nam nhật bản và sức hấp dẫn của tiếng nhật tại việt nam
- xác định các mục tiêu của chương trình
- xác định các nguyên tắc biên soạn
- khảo sát các chuẩn giảng dạy tiếng nhật từ góc độ lí thuyết và thực tiễn
- khảo sát chương trình đào tạo của các đơn vị đào tạo tại nhật bản
- khảo sát chương trình đào tạo gắn với các giáo trình cụ thể
- xác định thời lượng học về mặt lí thuyết và thực tế
- tiến hành xây dựng chương trình đào tạo dành cho đối tượng không chuyên ngữ tại việt nam
- điều tra đối với đối tượng giảng viên và đối tượng quản lí
- điều tra với đối tượng sinh viên học tiếng nhật không chuyên ngữ1
- khảo sát thực tế giảng dạy tiếng nhật không chuyên ngữ tại việt nam
- khảo sát các chương trình đào tạo theo những bộ giáo trình tiêu biểu
- nội dung cụ thể cho từng kĩ năng ở từng cấp độ
- xác định mức độ đáp ứng về văn hoá và chuyên môn trong ct
- phát huy những thành tựu công nghệ mới nhất được áp dụng vào công tác dạy và học ngoại ngữ
- mở máy động cơ lồng sóc
- mở máy động cơ rôto dây quấn
- các đặc tính của động cơ điện không đồng bộ
- hệ số công suất cosp fi p2
- đặc tuyến hiệu suất h fi p2
