Nghiên cứu tấn công RSA và xây dựng công cụ phân tích RSA
113
17
0
THÔNG TIN TÀI LIỆU
Thông tin cơ bản
| Tiêu đề | Nghiên Cứu Tấn Công RSA Và Xây Dựng Công Cụ Phân Tích RSA |
|---|---|
| Tác giả | Trần Đan Thư |
| Trường học | Đại Học Quốc Gia TP. HCM |
| Chuyên ngành | Khoa Học Tự Nhiên |
| Thể loại | Báo Cáo Nghiệm Thu |
| Năm xuất bản | 2015 |
| Thành phố | Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh |
| Định dạng | |
|---|---|
| Số trang | 113 |
| Dung lượng | 2,26 MB |
Nội dung
Ngày đăng: 11/10/2022, 07:08
HÌNH ẢNH LIÊN QUAN


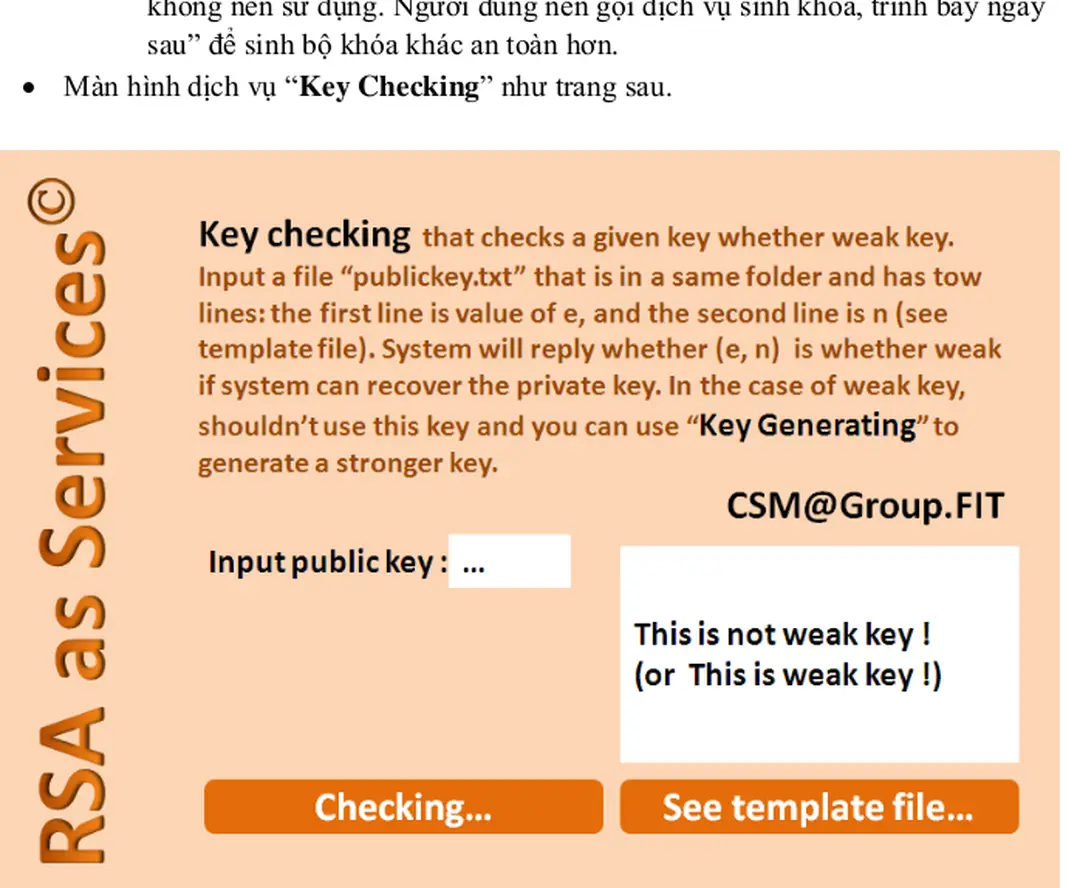

TỪ KHÓA LIÊN QUAN
TRÍCH ĐOẠN
Các khái niệm toán học
Ma-trận giả khả nghịch trên trƣờng hữu hạn Các phƣơng pháp phân tích thừa số Phƣơng pháp chia thửPhƣơng pháp sàng bậc ha
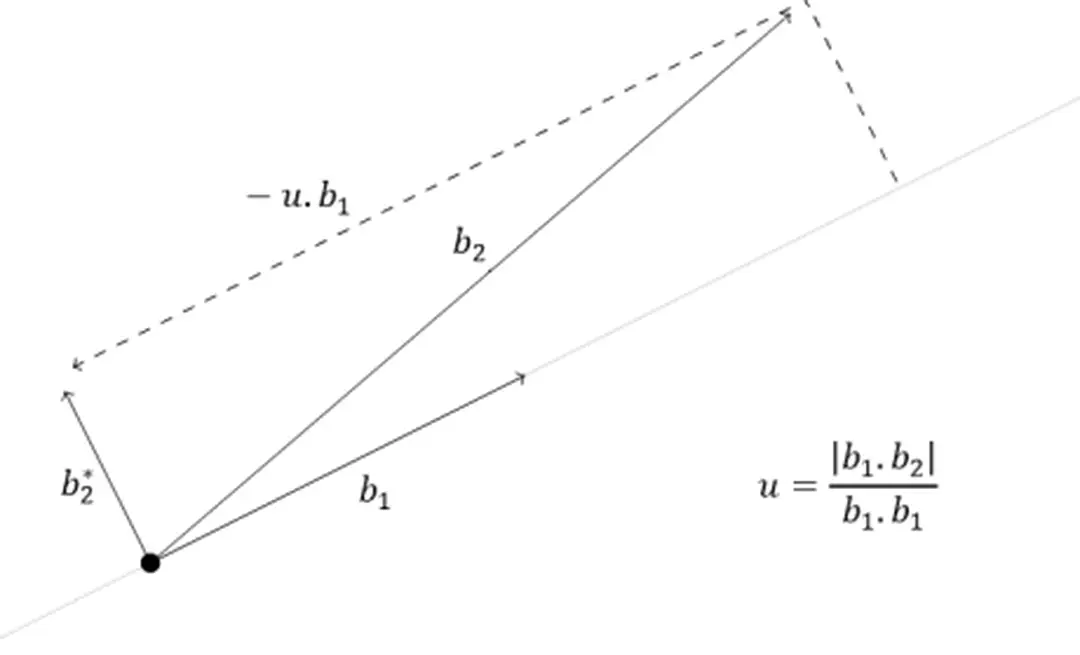
Lý thuyết dàn Định nghĩa về dàn Cơ sở lý thuyết Phụ lục C Phân tíc hn khi biết khoá cá nhân Phụ lục D Biên dịch và cấu hình hệ thống MSIEVE, GGNFSTÀI LIỆU CÙNG NGƯỜI DÙNG
-
137 740 2
-
143 1,1K 2
-
135 587 1
-
64 517 0
-
101 215 0
-
107 375 1
TÀI LIỆU LIÊN QUAN
-
113 17 0
-
3 7 0
-
89 11 0
-
20 25 0
-
225 40 0
-
20 67 0
-
83 28 0
-
83 24 0