chapter 5 disease and disorders of the eye and ear

Lecture Judgment in managerial decision making (8e) - Chapter 5: Framing and the reversal of preferences
... $240 and a 75 percent chance to lose $760 f a 25 percent chance to win $ 250 and a 75 percent chance to lose $ 750 Perceptions of Certainty Which of the following options you prefer? a a sure win of ... for $50 0,000 and estimate that you have a 50 percent chance of losing the case in court (expected value = –$ 250 ,000) However, the other side is willing to accept an out -of- court settlement of $240,000 ... 8e Chapter Framing and the Reversal of Preferences Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons The Asian Disease Problem Imagine that the United States is preparing for the outbreak of an unusual Asian disease
Ngày tải lên: 16/01/2020, 06:02

Lecture The management and control of quality - Chapter 5: Leadership and strategic planning
... development? ?and? ?deployment Understand? ?the? ?competitive environment? ?and? ?the? ? factors? ?and? ?strategic challenges that determine success,? ?and? ?gather? ?and? ?analyze a variety? ?of? ? external? ?and? ?internal data ... Creating? ?the? ?Leadership System An effective leadership system respects the? ?capabilities? ?and? ?requirements? ?of? ? employees? ?and? ?other stakeholders,? ?and? ? sets high expectations for performance and? ?performance improvements ... Customer? ?and? ?market requirements, expectations,? ?and? ?opportunities Technological? ?and? ?other innovations Organizational strengths? ?and? ?weaknesses Financial, societal, ethical, regulatory? ?and? ? other potential risks
Ngày tải lên: 04/11/2020, 23:34

Lecture tourism theory, concepts and models chapter 5 access and the spatial interactions of tourists
... Tourism Theory, Concepts and Models Bob McKercher and Bruce Prideaux Tourism Theories, Concepts and Models by McKercher and Chapter 5: Access and the Spatial Interactions of Tourists Tourism ... destination, then they cannot experience the attractions therein If they cannot move around the destination easily, their actions will be constrained Tourism Theories, Concepts and Time • The only ... Theories and Models © Bob McKercher and Bruce Prideaux All rights reserved 2021 Learning Objectives • • • • • • Distinguish between the resource and commodity values of time and analyse how they
Ngày tải lên: 21/10/2022, 18:48

Real-Time Digital Signal Processing - Chapter 5: Design and Implementation of FIR Filters
... given in the software package The addition of the second cosine term in (5. 3. 25) has the effect of increasing the width of the mainlobe (50 percent), but at the same time improving the peak-to-sidelobe ... attenuation is the passband of the filter, and the range of frequencies that is attenuated is the stopband. Thus the magnitude response of an ideal filter is given by jH!j 1 in the passband and jH!j ... coefficients of the FIR filter. This equation describes the output of the FIR filter as a convolution sum of the input with the impulse response of the system. The transfer function of the FIR filter
Ngày tải lên: 23/10/2013, 22:15

An Introduction to Intelligent and Autonomous Control-Chapter 5: Modeling and Design of Distributed Intelligence Systems
... external interactions The latter are the ones that determine the architecture of the DIS The origins of the model of the role can be traced back to the four stage model of the interacting decision ... including the null response, that is directed to the environment Thus, the interface between the system and the environment is composed of the sensors and the effectors Whether to include the sensors ... serve as candidate structures The reduction of the computational complexity of the problem to a tractable level is due to the presence of constraints and on the special structure of the role model
Ngày tải lên: 07/11/2013, 09:15

Learning DebianGNU Linux-Chapter 5: Installing and Configuring the X Window System
... as root and type the command: xf86config Figure 5. 1 shows the beginning of the xf86config dialog. As you can see, xf86config is a text-mode program; it does not support use of the mouse and it ... part of the desktop and a pop-up menu will appear From the menu, select the Exit, Logout, or Quit menu item X. .. Figure 5. 16, xf86config asks whether it should change the first line of ... on another computer, connected to the first via a network. With the advent of the Internet, which interconnected a sizable fraction of the computers on the planet, X achieved a new height of importance
Ngày tải lên: 07/11/2013, 10:15

Tài liệu Art of Surface Interpolation-Chapter 5:Solving special tasks In the next sections there are examples of interpolation problems, ppt
... 2118. 255 -2271 W-03 859 .634 1878.863 -2272 W-04 181. 357 151 9.776 -2292 W- 05 1940 .52 5 2187.171 -2277 W-06 2738.498 2292. 358 -2 255 W-07 2981 .51 7 23 75. 783 -2238 W-08 3344.232 9 35. 8 05 -2338 ... range from 1736 to 18 75 seconds at 258 53 points. It is obvious that the lower the value of reflection time, the higher the position of the rock structure boundary. The depth of the rock structure ... of the second surface is greater, the resulting value is the average. In the case of the second operation (%) the res- ulting value is the z-value of the second surface, but if the z-value of
Ngày tải lên: 21/01/2014, 07:20

báo cáo hóa học: " Measuring health-related quality of life in Hungarian children with heart disease: psychometric properties of the Hungarian version of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ 4.0 Generic Core Scales and the Cardiac Module" pptx
... mail, 52 5 families as subjects of the comparison group were recruited into the study (52 .5% ) Subjects included 268 boys (51 . 05% ) and 2 15 girls (40. 95% ) and 42 (8%) of unknown gender It was the mother ... 5- 18 years and 254 parents of children aged 2-18 years It was the mother who answered the questionnaire in 92 .52 % of the sample, and it was the father in 7.48% of the sample No parent in the patient ... child (5- 7) 111 21.14 58 58 .59 41 43. 75 5.26 41.41 12 Child (8-12) 160 30.48 72 50 .00 10.81 72 50 .00 16 Adolescent (13-18) All ages 102 52 5 19.43 100.00 57 268 59 .38 55 .49 10.00 39 2 15 40.63 44 .51
Ngày tải lên: 18/06/2014, 19:20

báo cáo hóa học:" The reliability, validity, and preliminary responsiveness of the Eye Allergy Patient Impact Questionnaire (EAPIQ)" docx
... 0.01604 0.36873 0 .54 369 -0.1 055 4 5 Dry eyes 0.492 05 -0.24760 0 .51 892 -0.12212 4 Itchy / burning eyes 0.46646 0.10921 0. 453 80 0.00162 32 Satisfaction with eye drops 0.01473 -0.0 054 8 -0.02048 0.93682 ... greater understanding of the impact of. .. authors read and approved the final manuscript 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Knight A: The role of levocabastine in the treatment of allergic ... presented as posters [4 ,5] . The objective of the present study was to further validate the questionnaire by investigating the psy- chometric properties of the EAPIQ in a sample of patients with ocular
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 15:20

WHEN THINGS GO WRONG – DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN docx
... think, see and hear, and to distinguish the ugly and the beautiful, the bad and the good, pleasant and unpleasant It is the brain too which is the seat of madness and delirium, of the fears and frights ... disorders and diseases of the brain, the advances in brain research provide hope in the form of their own understanding of what is going wrong and in the form of advances in novel therapies which ... – Diseases and Disorders of the Human Brain, Edited by Theo Mantamadiotis p cm ISBN 978- 953 -51 -0111-6 Contents Preface IX Part Chapter Chapter Syndromes and Disorders The Unique Properties of
Ngày tải lên: 28/06/2014, 11:20

DISORDERS OF THE VULVA AND VAGINA pps
... therapeutic... and arises in the labia (major and minor) in 65% of patients CHAPTER 20 DISORDERS OF THE VULVA AND VAGINA 59 1 and in the clitoris in 25% Over one third of tumors ... of metastases and subsequent.. .CHAPTER 20 DISORDERS OF THE VULVA AND VAGINA 58 1 cellulitis, and suppuration of the groin Involvement of apocrine glands establishes the ... commonly of the cervix) The average age of patients with vulvar cancer is 65, and 50 % of afflicted women are years 50 The cause of vulvar cancer is unknown, although HSV type 2 and
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 16:20

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 1 pps
... the function of the cochlea than of any other sensory organ C H A P T E R 1 Anatomy of the Ear 1 ABSTRACT 10 1 The ear consists of the outer ear, the middle ear and ... the inner ear 2 The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal 3 The skin of the ear canal is innervated by four cranial nerves: the trigeminal; the facial; the ... at the apex of the tympanic membrane (Fig 1. 5) The head of the malleus is suspended in the epitympanum The short process of the incus rests in the fossa incudo of the
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 2 ppsx
... measured in the place of the head. The effect of the head on the sound at the entrance of the ear canal is related to the size of the head and, the wavelength 2 of sound. This means that the “amplification” ... effect of the head on the sound pressure at the entrance of the ear canal depends on the frequency of the sound and on the angle of incidence of the sound (direction to the sound source). 6. The ... ear by an earphone may reach the other ear by bone conduction (cross transmission). CHAPTER 2 Sound Conduction to the Cochlea 3. HEAD, OUTER EAR AND EAR CANAL The ear canal, the pinna and the
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21
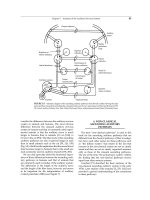
ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 4 potx
... pathways use the dorsal and medial division of the MGB as relay (Fig. 5. 10) [122]. These divisions of the MGB receive their input from the ICC and the ICX. The posterior division of the MGB (PO) ... to the surface of the floor of the fourth ventricle (Fig. 5. 15B) [72]. The other part of the olivocochlear system projects mainly to the contralateral cochlea and the fibers of that system travel ... in the early 1970s. Later studies of the anatomy [3, 270, 312] have provided a general understanding of the connections in these pathways. Chapter 5 Anatomy of the Auditory Nervous System 85 FIGURE
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 6 pot
... between the middle of that line and the vertex The origin of the vectors is the latency of the first peak in the dipole and the length is the relative strength of the. ... such as the cat, is approximately 0.8 cm long [59 ]. The difference between the latency of the N 1 of the AP and that of the response from the intracranial portion of the auditory nerve is the travel ... surface of the dorsal cochlear nucleus and the rostral portion of the floor of the lateral recess is the dorsal surface of the ventral cochlear nucleus [119] When the lateral
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 7 pot
... perforation depends on the size of the hole in the tympanic membrane and the size of the middle -ear cavity 210 Section III Disorders of the Auditory System and Their Pathophysiology ... 14: 419–442, 1 9 75 50 Evans EF and Nelson PG The responses of single neurons in the cochlear nucleus of the cat as a function of their location and the anaesthetic state Exp ... 0 .5 kHz, 0.3 kHz wide), for 5 min. Mean values from 18 subjects and standard error of the mean are shown as a function of the intensity of the noise. The TTS was measured 20 s after the end of
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 8 docx
... for loss of function of the active role of outer hair cells, that is to increase the sensitivity and frequency selectivity of the ear (cf. Chapter 3). The widening of the tuning of the basilar ... assumption Chapter 9 Hearing Impairment 221 BOX 9 .5 FREQUENCY OF GREATEST NIHL DEPENDS ON EAR CANAL LENGTH Studies of the correlation between the resonance fre- quency of the ear canal and the frequency ... spectrum. The amount of acquired hearing loss depends not only on the intensity of the noise and the duration of exposure but also on the character of the noise (fre- quency spectrum and time
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, AND DISORDERS OF THE AUDITORY SYSTEM - PART 9 pdf
... III Disorders of the Auditory System and Their Pathophysiology spectral bands of the visual spectrum The three kinds of photo pigment that are present in the cones of the ... tinnitus shows clearly that tinnitus can be generated in other places of the auditory system than in the ear. Perhaps the strongest argument against the ear always being the location of the physiologic ... that the olivocochlear efferent system may affect tinnitus. The fibers of the medial portion of the efferent bundle travel in the central por- tion of the inferior vestibular nerve, and join the
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 06:21

Báo cáo y học: "Chronic granulomatous disease: a review of the infectious and inflammatory complications" pot
... shown in the bott om of the figure. There are several components of NADPH oxidase: of these the cytochrome-b 55 8 heterodimer is located in the membrane and consists of the gp91 phox and p22 phox ... shown in the bottom of the figure. There are several components of NADPH oxidase: of these the cytochrome-b 55 8 heterodimer is located in the membrane and consists of the gp91 phox and p22 phox ... inflammatory disease. The disease is usually diagnosed in childhood and sometimes in early adulthood. Table 5 lists the infectious and Table 6 the inflammat ory consequences of CGD. Over 90% of the patients
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 13:22

Novel biodegradable cationic core shell nanoparticles for codelivery of drug and DNA chapter 5 conclusions and recommendations
... conditions, and they had a very stable coreshell structure because of the rigid chemical structure of the core-forming segment cholesterol The TEM scans of the micelles also evidenced the formation of the ... The presence of proteins in the blood affected the stability of the micelles An increased protein concentration yielded greater size of the micelles because of the adsorption of proteins on the ... immediately up to 4 25 nm from about 255 nm In the presence of 1% and 3% BSA, the size of the micelles changed in a narrow range from 1 35 to 161 nm This may be due to the presence of small BSA particles
Ngày tải lên: 16/09/2015, 15:54
Bạn có muốn tìm thêm với từ khóa: