Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed - M Ashby D Jones (1999) WW Part 7 doc

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 7 doc
... processing method could be introduced with economic benefits. Background reading M. F. Ashby and D. R. H. Jones, Engineering Materials I, 2nd edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1996. Further reading S. ... mm, or less. 14.4 Aluminium sheet is to be rolled according to the following parameters: sheet width 300 mm, starting thickness 1 mm, reduced thickness 0.8 mm, yield strength 100 M...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 4 docx
... is then warmed up to 75 °C and poured into the cold mould. When the solution touches the cold metal it cools very rapidly and becomes highly supersaturated. Ammonium chloride nuclei form heterogeneously ... be watched. The casting “material” used is ammonium chloride solution, made up by heating water to 50°C and adding ammonium chloride crystals until the solution just becomes saturated. Th...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 15 doc
... Index Moduli of ceramics and glasses 164, 177 composites 265, 266 foams 273 metals 12 polymers 224, 239 woods 278 Modulus of rupture 164, 181 Monel 7, 12 Mould design 308 Moulding 200, 2 57 Mullite ... polymerisation 228 Dendrites 65, 92, 352 Density of ceramics and glasses 164 foams 272 metals 12 polymers 224 woods 278 Design-limiting properties 289 Design methodology 291, 292 Diamond...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 2 potx
... worked or heat-treated into finished products; and by understanding these, shape and size can, to a large extent, be predicted. Background reading M. F. Ashby and D. R. H. Jones, Engineering Materials ... removed impurity from the left-hand end of the bar and dumped it at the right- hand end; that is, we have zone refined the left-hand part of the bar. Because we need to know how lon...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20
Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 4 pps
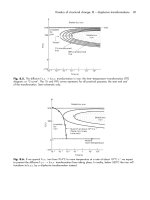
... (wt%) s y (MPa) Slowly cooled Quenched and aged 2000 Al + 4 Cu + Mg, Si, Mn 130 465 6000 Al + 0.5 Mg 0.5 Si 85 210 70 00 Al + 6 Zn + Mg, Cu, Mn 300 570 Work hardening Commercially pure aluminium (1000 ... Publishers, 1 973 . D. A. Porter and K. E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd edition, Chapman and Hall, 1992. M. C. Flemings, Solidification Processing, McGra...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 5 pps
... wear and tear. Untempered martensite is far too brittle for hammer heads. Having solved the immediate problem to our satisfaction we still wondered how the manufacturer had managed to harden the ... the hammers to go above 72 3°C are the ends: so only these parts can be hardened by the quench. The quenched heads are then dried and the ends are tempered by completely immersing the heads in .....
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 6 pps
... then re-assembled and poured. When the casting has gone solid it is removed by destroying the mould. Metal moulds are machined from the solid. They Production, forming and joining of metals 143 Chapter ... of a shaped casting will directly determine the strength of the finished article. Gas pores should be avoided, so the liquid metal must be degassed to remove dissolved gases (either by addin...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 7 doc
... sliding, and allowing the clay to be formed by hand or with simple machinery. When the shaped clay is dried and fired, one com- ponent in it melts and spreads round the other components, bonding ... 17. 1 shows that Table 17. 1 Specific moduli: ceramics compared to metals Material Modulus E Density r Specific modulus E/ r (GPa) (Mg m − 3 ) (GPa/Mg m − 3 ) Steels 210 7. 8 27 Al alloys 70...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20
- fundamentals of digital logic with vhdl design 2nd edition solutions
- fundamentals of digital logic with vhdl design 2nd solutions
- official ielts practice materials vol 2 free download
- electrical and electronics engineering materials pdf
- internetworking with tcp ip vol ii pdf
- professional css cascading style sheets for web design 2nd edition pdf
- engineering materials and their properties
- materials and energy in car design