validation of air handling systems

surface production operations - design of oil handling systems and facilities
... System Components 98 Single-Component Systems 99 Multicomponent Systems 101 Lean Gas Systems 103 Rich Gas Systems 103 Retrograde Systems 104 Application of Phase Envelopes 105 Black Oil Reservoir ... weight of dry air, which is a gas mixture consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, and small amounts of Argon 69 Gas Specific Gravity and Density 70 Example 3-3: Calculate the specific gravity of a natural ... number of people helped to make possible this revised third edition of Surface Production Operations, Volume 1—Design of Oil and Water Handling Facilities A real debt is owed to the 45,000-plus professional...
Ngày tải lên: 02/04/2014, 16:08

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 1 pps
... Fundamentals 479, Effect of Ambient Conditions 482, Effect of Air Compressor Speed 482, Single- vs Multi-Shaft Turbines 483, Effect of Air Contaminants 486 Environmental Considerations, 487 Air Pollution ... Convection The transfer of heat within a fluid as the result of mixing of the warmer and cooler portions of the fluid is convection For example, air in contact with the hot plates of a radiator in a ... cold air is drawn off the floor of the room The room is heated by convection It is the mixing of the warmer and cooler portions of the fluid that conducts the heat from the radiator on one side of...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 2 doc
... 12 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and facilities Figure 2-2 Change in AT over distance, counter-current flow of fluids Since the temperature of both fluids changes as they ... the center of the tube to laminar flow at the tube surface The inside film coefficient can be calculated from: 16 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Table 2-1 Characteristics of Tubing ... Edition.) The mass velocity of a fluid in pounds per hour per square foot can be calculated from 22 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 2-6 Thermal conductivities of hydrocarbon liquids...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... cross-section of the shell, because the fluid that is in the shell has to be able to come 50 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities over the top of the baffle and under the bottom of the next ... types of baffles to help direct the flow of both tube-side and shell-side fluids Pass partition baffles force the fluid to flow through several groups of parallel tubes Each of these groups of tubes ... 9.5 11.0 12,3 13.5 14.6 15.6 17.4 46 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems; and Facilities For natural draft fire tubes, the minimum cross-sectional area of the fire tube is set by limiting the heat...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 4 pdf
... when the outside surface area of the bare tube (neglecting fins) is used in the heat 76 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 3-15 Side elevations of air coolers (From Gas Processors ... 7.981 72 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 3-12 Double pipe exchanger (text continued from page 65) two fluid streams flow in parallel between alternate pairs of plates In addition ... which case air would be blown horizontally through the cooler Forced -air exchangers have tube lengths of to 50 ft and tube diameters of % to IM-in The tubes have fins on them since air is non-fouling...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 5 pps
... downstream of the choke, which assures that the enthalpy of the mixture of gas and liquid upstream of the choke equals the enthalpy of the new mixture of more gas and less liquid downstream of the ... formation (Courtesy of Smith Industries, Inc.) 100 Design of GAS-HANDLINCr Systems and facilities by Figure 4-6 The graph shows the water content in pounds of water per MMscf of saturated gas at ... Mara of Paragon Engineering Services, Inc 109 110 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities LTX UNITS These units are designed to allow hydrates to form and to melt them with the heat of the...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 6 potx
... number of passes of coil Therefore, the correct selection of coil length also requires determining the length of the shell and number of passes As the shell length decreases, the number of passes ... exchanger 134 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities The liquids leaving the bottom of the tower have undergone a series of stage flashes at ever-increasing temperatures, driving off the light ... Figure 4-6, we have: 126 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities lb water/MMscf of wet gas at reservoir conditions (8,000 psig and 224°F) lb water/MMscf of wet gas at 1,000 psig and 75...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 7 ppsx
... K S Chiou of Paragon Engineering Services, Inc 151 152 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Table 7-1 Physiological Effects of H2S Concentrations in Air Concentrations in Air Percent ... height of the tower can be derived using manufacturer's data for the particular device The height of the tower is a function of the number of theoretical stages and of the efficiency of the actual ... number of moles of component n in feed Ln = total number of moles of component n in the bottom liquid (fl-C4 split) = assumed moles of component n-C4 in bottom liquid divided by moles of n-C4...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 8 doc
... of DEA ranges up to 35% by weight compared to only 20% for MEA Loadings for DEA systems range to 0.65 mole of acid gas per mole of DEA compared to a maximum of 0.4 mole of acid gas per mole of ... reclaimer DGA systems typically circulate a solution of 50-70% DGA by weight in water At these solution strengths and a loading of up to 0.3 mole of acid gas per mole of DGA, corrosion in DGA systems ... levels of acid gas to be achieved easily A stripper is required to reverse the reactions of the DIPA with CO2 and H2S This adds to the cost and complexity of the sys- 172 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 9 pdf
... weight of 26 that is in equilibrium with a 3% brine at a pressure of 3,000 psia and a temperature of 150°R From Figure 8-1 at a temperature of 150°F and pressure of 3,000 psia there is 104 Ib of ... degradation, a variety of contaminants will begin to accumulate in an amine system The method of removing these depends on the amine involved 190 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities ... conditions of atmospheric pres- 204 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities sure and high temperatures The gas will adsorb the waler from the glycol by lowering the partial pressure of the...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 1 Part 10 pdf
... Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 8-12 Effect of stripping gas on glyco! concentration dehydrators are designed for approximately three gallons of glycol per pound of water ... cracks Liner cracks will per- 232 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities mit some of the wet gas to bypass the desiccant bed Only a small amount of wet, bypassed gas is needed to cause ... 4) This is: Gas Dehydration 215 Figure 8-15 Various types of packing (Courtesy: McGraw-Hill Book Company.} 216 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 8-16 Glycol concentration vs...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 1 docx
... design on the basis of 6% loading Sorbeads weigh approximately 49 lb/ft3 (bulk density) The required weight and volume of desiccant per bed would be: 238 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities ... the heating value of gas The value of the increased volume of liquids sales may be significantly higher than the loss in gas sales revenue because of a decrease in heating value of the gas *Reviewed ... processing Often it is more economical to separate the liquid into its various components and sell it as 250 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 9-4 Simplified flow diagram of a fractionation...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 2 pps
... calculation of horsepower and number of stages depends upon the choice of type of compressor, and the type of compressor depends in part upon horsepower and number of stages A first approximation of the ... consideration of the advantages and disadvantages listed earlier In addition, local foundation conditions, type of drivers available, cost of fuel, availability of spare 272 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems ... service 266 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Disadvantages • Must have clean air or gas «Takes to 20% more horsepower than reciprocating * Uses ten times the oil of a reciprocating...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 3 potx
... constructed of a number of pairs of rings, as shown in Figure 11-14 The gas pressure is higher on one side of each ring This compresses the rings against the sealing area Each pair of rings consists of ... The effects of the seat area, the lift area, and the flow paths are automati- 302 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figyre 11-16 Cut-away view of poppet valve {Courtesy of 0resser-Roncf ... crankcase There are drains and vents off the distance piece and off the packing, so if there is a packing failure, the high-pressure gas has 294 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 4 pdf
... lubrication system Splash lubrication systems are 314 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities the least expensive and are used in small air compressors Forced-feed systems are used for almost all ... with a minimum clearance of 17.92%, a rod load limit of 25,000 Ib, and rod diameter of 1.75 in Assume k = 1.26, Zs = 0.88, and Zd = 0.85 322 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure ... 334 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 12-1 Pressure vessel shapes nameplate on the vessel will be stamped to signify it has met the requirements of the Code One of these requirements...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 5 pps
... The weight of one 2:1 ellipsoidal head is approximately: The weight of a cone is: a = one half the cone apex angle 339 340 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities The weight of nozzles ... lb (b) Shell: Height of cone = tan 30 = 8.7 ft Length of shell = 12 + 8.7 = 20.7 ft Weight of shell = (11)(120)(0.8125)(20.7) = 22,200 Ib 353 354 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities ... Protection Pressure vessels handling salt water and fluids containing signficiant amounts of H2S and CO2 require corrosion protection Common corro- 350 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 6 docx
... of the disc Thus, the forces created by the back-pressure always cancel and not affect the set point, Figure 13-4 Balanced-bellows relief valve (Courtesy of API.) 364 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems ... Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities EXAMPLE PROBLEM 13-1 Given: Qg = maximum flow = lOMMscfd MW = molecular weight of gas = 23.2 Z = compressibility factor = 0.9334 k = ratio of specific ... Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities EXAMPLE PROBLEM 13-2 Given: Qg MW Z k T P = maximum flow = 50 MMscfd = molecular weight of gas = 17.4 = compressibility factor = 0.9561 = ratio of specific...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 7 docx
... Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities nating one of the conditions Since no condition can be eliminated with absolute certainty, an attempt is made to minimize the occurrence of each of the ... would be required, given the degree of reliability of shutdown systems and the consequences 400 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities of failure However, it is more costly in engineering ... ANNUNCIATION SYSTEMS These systems give early warning of impending trouble to allow personnel to take corrective action prior to a shut-in, and provide informa- 406 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20
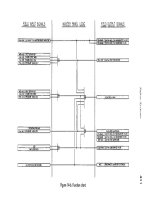
ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 8 docx
... replace Because of the erosive action of the fluid when the valve is throttling, they should not be used for on/off service, A tight seal may not be possible, 434 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and ... common general-purpose on/off valves in production facilities (text continued from page 430) 428 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Table 15-2 Example Specifications of Pipe, Valves/ and ... valve (Courtesy of Cameron Iron Works, Inc.] Figure 15-2 Cutaway of plug valve (Courtesy ofXomox Corp.) 432 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Plug valves usually require lubrication...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20

ARNOLD, K. (1999). Design of Gas-Handling Systems and Facilities (2nd ed.) Episode 2 Part 9 ppt
... lines, oil treating systems, fire water systems, and produced water treating systems Offshore applications include fire water and utility systems The primary advantages are ease of field installation ... conditions 442 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure 15-10 Wafer check valve (Courtesy of TRW Mission Drilling Products Division.} Figure 15-11 Lift check valve (Courtesy of Jenkins Bros.} ... Piston check valve (Courtesy of Whealtey Pump and Valves, Inc.] Figure 15-13 Ball check valve (Courtesy of Wheatiey Pump and Valves, Inc.] 444 Design of GAS -HANDLING Systems and Facilities Figure...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 02:20