an introduction to financial option valuation solutions

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_13 pot
... PDE (23.9) and (23.11) to give 1 2 (I +... Notes and references As we mentioned in Chapter 23, it is possible to convert the Black–Scholes PDE for European calls and puts into the heat ... of how to transform the Black–Scholes... transform the Black–Scholes PDE (8.15) into standard heat equation form (23.2) can be found, for example, in (Nielsen, 1999, Section 6.7) and (Wilmott ... differencing in time. The Crank–Nicolson method uses a clever trick to achieve second order in time without the need to deal with more than two time levels. To derive the Crank–Nicolson method, we
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_14 pot
... (2002) Monte Carlo valuation of American options. Mathematical Finance, 12:271–286. Rogers, L. C. G. and E. J. Stapleton (1998) Fast accurate binomial pricing of options. Finance and Stochastics, 2:3–17. ... London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, 5, 135 London Stock Exchange, 50 Long-Term Capital Management, 93–94 lookback option, 191–192, 196 low discrepancy sequences, 233 market ... questions, be on the phone, and fill the seminar room. TOM COLEMAN, Financial Engineering News, September/October 2002 References Almgren, Robert F. (2002) Financial derivatives and partial differential
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_8 pdf
... the case of an American call option. Show that the Black–Scholes European call option formula (8.19) satisfies the relevant analogues of (18.2)–(18.6). Deduce that an American call option has the ... European The picture illustrates that barrier options can be significantly cheaper than Europeans The up-and-out call has a limited up-side – the 19.3 Lookback options 191 Up–and–out European Call ... deals with points (i) and (iii). 180 American options 18.6 Monte Carlo for an American put We have seen that the binomial method has a natural extension from European to American options. The same
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 04:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_9 doc
... σ is computed in order to value an option, then a widely quoted rule of thumb is to make the historical data time-frame Mt equal to that of the option: to value an option that expires in six ... discrete random variable. In the [...]... if the covariance is positive then X and Y tend to be smaller than their means or larger than their means at the same time Similarly, if the covariance ... example To illustrate the use of antithetic variates,... important aspects of practical option valuation, and it remains an active research topic, see (Poon and Granger, 2003), for example More
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 04:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_11 pdf
... try to correct this imbalance. Here, we reduced N t to 94, so k ≈ 0.032 and ν ≈ 0.63. We see that the numerical solution has de- veloped oscillations that render it useless as an approximation to ... simplifies to 0 ≤ ν sin 2 ( 1 2 βh) ≤ 1 2 . For βh ∈ [−π, π] the quantity sin 2 ( 1 2 βh) takes values between 0 and 1, and hence stability in the sense of von Neumann for FTCS is equivalent to ν ≤ ... differencing in time. The Crank–Nicolson method uses a clever trick to achieve second order in time without the need to deal with more than two time levels. To derive the Crank–Nicolson method, we
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 04:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_12 pptx
... (2002) Monte Carlo valuation of American options. Mathematical Finance, 12:271–286. Rogers, L. C. G. and E. J. Stapleton (1998) Fast accurate binomial pricing of options. Finance and Stochastics, 2:3–17. ... London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, 5, 135 London Stock Exchange, 50 Long-Term Capital Management, 93–94 lookback option, 191–192, 196 low discrepancy sequences, 233 market ... questions, be on the phone, and fill the seminar room. TOM COLEMAN, Financial Engineering News, September/October 2002 References Almgren, Robert F. (2002) Financial derivatives and partial differential
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 04:20

Financial calculus Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_3 doc
... understand the factors that influence and move option prices butinthe absence of an ability to forecast these factors the transformation into money remains non-trivial. DILIP B. MADAN (Madan, 2001) Evidence ... a stock option Grasping the intimate relation between an option and the underlying stock, Merton completed the puzzle with an elegantly mathematical flourish Then he graciously waited to ... able to transform this knowledge into money. Finance is consistent in its ability to build good models and consistent in its inability to make easy money. The purpose of the model is to understand
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 09:20

Financial calculus Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_4 pptx
... of us to carry out hedging. On one side there is a large group of investors who view options as an excellent means to alleviate their exposure to risk, and another large group who see options ... willing to accept some risk may value an option differently to the Black–Scholes formula However, if you are selling the option and wish to hedge in order to eliminate risk (and if ... drift µB and volatility σ Suppose the speculators wish to take a naked, long position on a European call option – that is, they wish to buy the option without performing any accompanying...
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 09:20
Financial calculus Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_5 doc
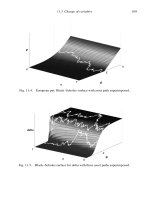
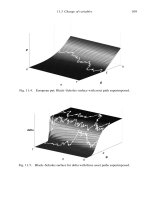
... is to scale the option values by the asset price, by letting c := C S , for a call option, and p := P S , for a put option. In these new variables, d 1 and d 2 in (8.20) and (8.21) simplify to ... applies to a European put option, as in Figure 11.4. P11.2. Edit ch11.m so that it applies to the delta of a European call option, as in Figure 11.5, and investigate the use of surf, surfc and waterfall ... points to make. (i) Formulas (12.2) and (12.4) were derived without any reference to the idea of hedging to eliminate risk. (ii) Formulas (12.2) and (12.4) were derived without any reference to the
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 09:20

Financial calculus Introduction to Financial Option Valuation_6 ppt
... straightforward to describe and implement, and, as we will see in Chapters 18 and 19, has the advantage that it is readily adapted to a range of non-European options for which no analytical formula ... computing an expected value The idea of using pseudo-random number generators to compute estimates of expected values was touched on in Chapter 4 Here we pull these two threads together and introduce ... partial derivatives of the option value with respect to various... means to compute option values in cases where no analytical formulas are available 15.2 Monte Carlo To begin, we consider
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 09:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_1 pot
... intentionally left blank AN INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL OPTION VALUATION Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation This is a lively textbook providing a solid introduction to financial option valuation for ... contributions to a broad range of problems in numerical analysis AN INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL OPTION VALUATION Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation DESMOND J HIGHAM Department of Mathematics ... for an American put Notes and references Program of Chapter 18 and walkthrough 174 176 177 180 182 183 19 Exotic options 19.1 Motivation 19.2 Barrier options 19.3 Lookback options 19.4 Asian options...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_3 pptx
... rand and randn to generate U(0, 1) and N(0, 1) samples, respectively To make the experiments reproducible, we set the random number generator seed to 100; that is, we used rand(‘state’,100) and ... samples and N(0,1) quantiles N(0,1) samples and U(0,1) quantiles 5 0 −5 −5 −5 −5 U(0,1) samples and N(0,1) quantiles U(0,1) samples and U(0,1) quantiles 1.5 0.5 −0.5 −5 −5 −1 −1 Fig 4.4 Quantile–quantile ... simulation to experiment with and visualize our ideas, and also to estimate quantities that cannot be determined analytically This chapter introduces the tools that we will apply 4.2 Pseudo-random...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_4 ppt
... data analysis Many exchanges have informative websites, including the American Stock Exchange: www.amex.com/, the Chicago Board Options Exchange: www cboe.com/Home/, the London Stock Exchange: ... known to investors, and hence any change in the price is due to new information We may build this into our model by adding a random ‘fluctuation’ increment to the interest rate equation and making ... way to compute a quantile–quantile plot, as seen in Figures 4.4, 4.6 and 5.3 It is listed in Figure 5.4 We use MATLAB’s N(0, 1) pseudo-random number generator, randn The line samples = randn(M,1),...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_5 ppt
... see (Rogers and Zane, 1999), for example A completely different approach is to abandon any attempt to understand the processes that drive asset prices (in particular to pay no heed to the efficient ... the company and has many insights into the practical issues involved in collecting and analysing vast amounts of financial data EXERCISES 7.1 7.2 Confirm the results (7.4) and (7.5) By analogy ... able to transform this knowledge into money Finance is consistent in its ability to build good models and consistent in its inability to make easy money The purpose of the model is to understand...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20
An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_7 pdf
... , S for a call option, p := P , S for a put option and In these new variables, d1 and d2 in (8.20) and (8.21) simplify to d1 = m τ + τ and d2 = m τ − , τ (11.1) and, from (8.19) and (8.24), the ... applies to a European put option, as in Figure 11.4 P11.2 Edit ch11.m so that it applies to the delta of a European call option, as in Figure 11.5, and investigate the use of surf, surfc and waterfall ... points to make (i) Formulas (12.2) and (12.4) were derived without any reference to the idea of hedging to eliminate risk (ii) Formulas (12.2) and (12.4) were derived without any reference to the...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_8 pptx
... two threads together and introduce the Monte Carlo approach to valuing an option As we will see in Chapter 19, this provides a powerful means to compute option values in cases where no analytical ... showed that valuing an option can be regarded as computing an expected value The idea of using pseudo-random number generators to compute estimates of expected values was touched on in Chapter ... look at the implied volatility for call options traded on the London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange (LIFFE), as reported in the Financial Times on Wednesday, 22 August 2001...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_9 pot
... Chapter that led to the Black–Scholes PDE can be adapted to cover an American put option We write P Am (S, t) to denote the American put option value at asset price S and time t, and use (S(t)) ... reach, and puts a strain on computational methods 18.2 American call and put An American option is like a European option except that the holder may exercise at any time between the start date and ... better than gaining S(t) − E at time t Since it is never optimal to exercise an American call option before the expiry date, an American call option must have the same value as a European call option...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation Mathematics Stochastics and Computation_1 doc
... arguments to those above can be used to obtain simple upper and lower bounds on the values C and P of European call and put options To study the call option, consider two portfolios: π A : one call option ... than π B at time then it would be possible to sell π A (that is, sell the call option and borrow the cash) and buy π B (that is, buy one put option and one share) This brings us an instantaneous ... 1 Options OUTLINE • European call and put options • payoff diagrams • how and why options are traded 1.1 What are options? Throughout the book we use the term asset to describe any financial...
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 07:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation Mathematics Stochastics and Computation_4 docx
... see (Rogers and Zane, 1999), for example A completely different approach is to abandon any attempt to understand the processes that drive asset prices (in particular to pay no heed to the efficient ... the company and has many insights into the practical issues involved in collecting and analysing vast amounts of financial data EXERCISES 7.1 7.2 Confirm the results (7.4) and (7.5) By analogy ... able to transform this knowledge into money Finance is consistent in its ability to build good models and consistent in its inability to make easy money The purpose of the model is to understand...
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 07:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation Mathematics Stochastics and Computation_9 ppt
... 19.6 19.5 Bermudan and shout options A Bermudan option differs from the corresponding American option in only one respect While the American option allows the holder to exercise at any time in [0, ... lookbacks, barriers and Asians early exercise options: Bermudans and shouts Monte Carlo and binomial methods 19.1 Motivation So far, we have seen European options and American-style options A bewildering ... the case of an American call option Show that the Black–Scholes European call option formula (8.19) satisfies the relevant analogues of (18.2)–(18.6) Deduce that an American call option has the...
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 07:20
Bạn có muốn tìm thêm với từ khóa: