Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 10

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 10
... linear y acceleration → a of point P on a at rotating rigid body has two perpendicular components, the P a tangential component at and ar the radial component ar O x Rotation axis The magnitude of ... concept of torque After that we treat some general cases where the axis of rotation is not fixed in space In these cases, rigid bodies can undergo both rotational and transla...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 01
... thanks to my wife and two sons Tarek and Rami for their ongoing support and encouragement I also owe special thanks to my colleague and friend Prof Rasmussen for his invaluable contributions to ... hafez. radi@gmail.com Acknowledgments from Prof John O Rasmussen I would like to thank Prof Radi for the opportunity to join him as coauthor I am grateful to the many teacher...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:18

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 02
... atoms of hydrogen (11H), each of which has a mass of u, and one atom of oxygen (168 O) , that has a mass 16 u, approximately (a) What is the mass of one molecule of water in units of kilograms? ... dimension of the inverse of time (22) Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied and inversely proporti...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 03
... used most often in solving problems for the case of constant acceleration 54 Motion in One Dimension Table 3.1 Equations for motion with constant acceleration Equation Missing quantity Equation ... 3.5 Motion in One Dimension Constant Acceleration In many common types of one-dimensional motion, the acceleration is constant (or we say uniform) In this case, the average acceleration eq...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 04
... assumptions, we find that: (1) the horizontal motion and vertical motion are independent of each other and (2) the two dimensional path of a projectile (also called its trajectory) is always a parabola ... acceleration a as follows: Instantaneous acceleration → The instantaneous acceleration, a , of a particle is defined as the limiting value → of the ratio v→/ t when t...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 05
... The Cause of Acceleration and Newton’s Laws 105 Newton’s Third Law of Motion Forces come in pairs For example, if you lean against a wall with a certain force, the wall reacts and pushes back on ... velocity → v of a particle changes in both direction and magnitude, the acceleration → a can be decomposed to a radial component vector → a r and a tangential compon...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 06
... (decelerating), see Fig 5.44 A person stands on a scale in that elevator, and hence pushes downwards on the scale The scale also reacts with an upward normal force The maximum 134 Force and Motion and ... block m2 is before block m1 and the same force acts on m2 (13) Two toys of masses m1 = 40 g and m2 = 120 g are connected by a massless rope and lie on a horizontal fric...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19
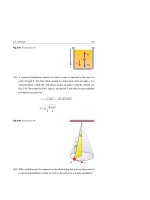
Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 07
... to point b along path and then back to point a along path i.e., the work done by a conservative force on a particle moving from a to b along path is the same as from a to b along path In words: ... (a) A conservative force acts on a particle moving from point a to point b by following either path or path (b) A conservative force acts on a particle moving in a round tri...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 08
... has one of its ends fixed and the other attached to a block of mass m that rests on a frictionless horizontal surface The application of a horizontal force F on the block causes the spring to stretch ... a constant acceleration a of 1.5 m/s2 that produces a speed v = at? (42) A constant horizontal force F = 20 N acts on a block of mass m = kg resting on a horizon...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 09
... Translational motion of the CM CM CM CM Translational motion of the CM plus rotational motion about the CM CM (a) (b) Fig 7.12 (a) A top view of the translational motion of the CM of a wrench over a ... Center of Mass (CM) Until now, we have dealt with translation motion of an object that can be approximated by a point particle In fact, real objects can undergo both tran...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:19

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 11
... Rotational Motion 8.6 Rotational Dynamics; Torque Rotational dynamics is the study of rotational motion and the causes of changes in motion Just as linear motion is analogous to rotational motion ... the action of these components passes through the axis of rotation 8.7 Newton’s Second Law for Rotation 243 Parallel-Axis Theorem If we calculate the moment of inertia of a bod...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 12
... the moment of inertia of the platform about the rotational axis is constant during the man’s walk and given by Ip = 21 MR2 In addition, the initial and final moment of inertia of the man about ... constant in both magnitude and direction 278 Angular Momentum We can now state that the total energy, total linear momentum, and total angular momentum of an isolated system all r...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 13
... (7) A canonical pendulum consists of a bob of mass m attached to the end of a cord of length The bob whirls around in a horizontal circle of radius r at a constant speed v while the cord always ... and gas A solid is a highly ordered array of atoms or molecules that are bound securely by mutual electrical forces A liquid is a crowded assembly of mobile atoms...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 14
... downwards on a small piston of area A1 The pressure will be transmitted through an incompressible fluid which then exerts an output force F2 on a larger piston of area A2 , balancing the load ... walls Fig 10.20 A stream tube formed by the streamlines The flow rate of fluid at the cross sections A1 and A2 is the same Stream tube A2 A1 Figure 10.21 shows two cross-sectional...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20

Hafez a radi, john o rasmussen auth principles of physics for scientists and engineers 15
... ideal gas model and the low-pressure gas is commonly referred to as an ideal gas Most gases at room temperature and atmospheric pressure behave as ideal gases Equation of State of an Ideal Gas One ... Chap 1); then the molar mass M of 12 C is 12 kg/kmol and contains NA atoms For a molecular substance or chemical compound, we add up the molar mass from its molecular formula Thu...
Ngày tải lên: 05/10/2016, 11:20
- a guide to microsoft excel 2007 for scientists and engineers free pdf
- a guide to microsoft excel 2007 for scientists and engineers pdf download
- a guide to microsoft excel 2007 for scientists and engineers download
- a guide to microsoft excel 2007 for scientists and engineers solutions
- a guide to microsoft excel 2007 for scientists and engineers 1st edition
- harrisons principles of internal medicine selfassessment and board review