Introduction to Elasticity Part 14 ppt

Introduction to Elasticity Part 14 ppt
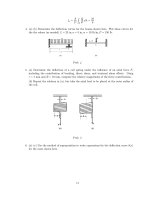
... firmly bonded to an aluminum part (α =2.5 × 10 −5 K −1 ) at 180 ◦ C. Calculate the minimum defect size needed to initiate cracking in the resin on cooling to 20 ◦ C. Take α in Eqn. 5 to be 2/π for ... stress along the top surface and a tensile stress along the bottom (see Fig. 3). After the axle has rotated a half turn, the bottom becomes the top and vice versa, so the stresses on a...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 4 ppt
... force vector F: T = r × F (6) This vector is in a direction given by the right hand rule, and is normal to the plane containing the point O and the force vector. The torque tending to loosen ... cross-sectional dimension b × h, are to be glued together using a tongue-and-groove joint as shown in Fig. 3, and we wish to estimate the depth d of the glue joint so as to make the joint ap...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20
Introduction to Elasticity Part 8 pptx
... Axes It is important to be able to transform the axes to and from the “laboratory” x − y frame to a natural material frame in which the axes might be labeled 1 − 2 corresponding to the fiber and transverse ... loads: 9 enter modulus in fiber direction (enter -1 to stop): -1 define layup sequence, starting at bottom (use negative material set number to stop) enter material set n...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 9 pptx
... the stress intensity factor, with units of Nm −3/2 or psi √ in. (The factor π seems redundant here since it appears to the same power in both the numerator and denominator, but it is usually included ... be extremely difficult to fit solutions of the governing equations to them. One approach to this impasse is the experimental one, in which we seek to construct a physical laboratory mo...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 1 docx
... the loads to be applied to the structure are known at the outset, and we wish to compute how much material will be needed to support them. As a very simple case, let’s say we wish to use a steel ... would be too small in cross-sectional area to support the much greater loads they would be called upon to resist. When reporting the strength of materials loaded in tension, it is cu...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 2 docx
... stretches to λ d , after which the engineering stress there would have to rise to stretch it further. But this stress is greater than that needed to stretch material at the edge of the neck from λ Y to ... material, but it is also possible to arrange for them to be oriented preferentially in the direction expected to have the highest stresses. Such a material is said to be a...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 5 pot
... pseudovector form. This relation serves to define the stress concept as an entity that relates the traction (a vector) acting on an arbitrary surface to the orientation of the surface (another vector). ... quantities). Recall Cauchy’s relation in matrix form: [σ]ˆn = T UsingEqn.14totransformtheˆnand T vectors into their primed counterparts, we have 8 1. Draw the stress square, noting the v...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 6 pps
... said to be orthotropic. 6 Constitutive Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 October 4, 2000 Introduction The ... induced in beams by bending loads took many years to develop. Galileo worked on this problem, but the theory as we use it today is usually credited principally to the great mathema...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21
Introduction to Elasticity Part 7 pdf
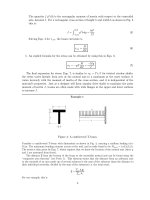
... radius r 1 to r 2 over the length L. We wish to determine the deflection caused by a force F applied to the free end of the beam, at an angle θ from the horizontal. Turning to Maple to avoid the ... about the neutral axis. The parameter Q(y) is notorious for confusing persons new to beam theory. To determine it for a given height y relative to the neutral axis, begin by sketchi...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21