Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 2 ppsx

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 2 ppsx
... circumferential speed of the journal U 2 is along the inclined surface, and Eq. 2. 20 becomes: ∂ ∂x h 3 ∂p ∂x + ∂ ∂z h 3 ∂p ∂z = 6µ (U 1 + U 2 ) ∂h ∂x + 2V 2 (2. 24) It is this form of the equation ... (see Chapter 5). 22 2 Foundations of Hydrodynamic Lubrication surface of 2. 10a,ba and the upper surface of 2. 10a,bb are equivalent, and they are called the moving...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 1 docx
... Basic Equations 121 6 .2 Finite Element Solution of the Basic Equations 122 6 .2. 1 Reynolds’ Equation 122 6 .2. 2 Equation of Balance for the Foil 125 Contents IX 6 .2. 3 SolutionProcedure 126 6.3 Characteristics ... 8 2 Foundations of Hydrodynamic Lubrication 9 2. 1 Tower’s Experiment . . . . 9 2. 2 Reynolds’ Theory of Hydrodynamic Lubrication . . 11 2. 2.1 Interpretation...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 3 docx
... φ) 3 = 1 (1 − κ 2 ) 5 /2 ϕ − 2 sin ϕ + κ 2 ϕ 2 + κ 2 4 sin 2 (3.11) J 2 = dφ (1 + κ cos φ) 2 = 1 (1 − κ 2 ) 3 /2 ϕ − κ sin ϕ (3. 12) J 1 = dφ 1 + κ cos φ = ϕ (1 − κ 2 ) 1 /2 (3.13) Now, ... distribution, becomes: p(ϕ) = 6µUR c 2 1 (1 − κ 2 ) 3 /2 ϕ − κ sin ϕ − h m c(1 − κ 2 ) 5 /2 ϕ − 2 sin ϕ + κ 2 ϕ 2 + κ 2 4 sin 2 + C 2 (3.14)...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 4 pps
... be: P = h 2 h 1 pdx= xp h 2 h 1 − h 2 h 1 x dp dx dx = − h 2 h 1 x dp dx dx (4.14) = 6µU h 2 h 1 x 1 h 2 − h m h 3 dx = 6µUB 2 h 2 2 h 2 h 1 ¯x ⎛ ⎜ ⎜ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ 1 h 2 − h m h 3 ⎞ ⎟ ⎟ ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ d ... as follows: p(¯x) = 6µUB h 2 2 (m − 1)(1 − ¯x)¯x (m + 1)(m − m ¯x + ¯x) 2 ≡ 6µUB h 2 2 ¯p(¯x) (4. 12) h m = 2m m + 1 (4.13) Nondimensional pressure ¯p(¯x) on th...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 5 potx
... 2 ˙ θ) (2 + κ 2 )(1 − κ 2 ) + 2 κ (1 − κ 2 ) 3 /2 π 2 − 8 π (2 + κ 2 ) (5 .23 ) P θ = 6µ R j c 2 LR j πκ(ω − 2 ˙ θ) (2 + κ 2 )(1 − κ 2 ) 1 /2 + 4κ˙κ (2 + κ 2 )(1 − κ 2 ) (5 .24 ) where the ... 4)κ 0 2 1 κ 0 − κ 0 2 + κ 0 2 + κ 0 1 − κ 0 2 (5.37) K xy = − π 1 − κ 0 2 κ 0 π 2 − (π 2 − 4)κ 0 2 (5.38) C xx = − 2( 2 + κ 0 2...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21
Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 6 pot
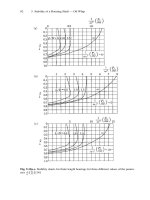
... X 1 and X 2 of second order only, as: p = p 0 + p 1 X 1 + p 2 X 2 + p 3 X 3 + p 4 X 4 + p 11 X 1 2 + p 12 X 1 X 2 + p 22 X 2 2 + p 13 X 1 X 3 + p 14 X 1 X 4 + p 23 X 2 X 3 + p 24 X 2 X 4 (5.84) where X 3 = dX 1 dt , ... pressure coefficients. These coefficients are defined as: p 1 = ∂p ∂X 1 0 , p 2 = ∂p ∂X 2 0 , ··· p 24 = ∂ 2 p ∂X 2 X 4 0 (5.86) 92 5 Stab...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 7 pot
... d 124 X 2 X 4 (5.94) M dX 4 dt = − d 21 X 1 − d 22 X 2 − d 23 X 3 − d 24 X 4 − d 21 1 X 2 1 − d 21 2 X 1 X 2 − d 22 2 X 2 2 − d 21 3 X 1 X 3 − d 21 4 X 1 X 4 − d 22 3 X 2 X 3 − d 22 4 X 2 X 4 (5.95) where the d’s are the dynamic ... d 11 X 1 − d 12 X 2 − d 13 X 3 − d 14 X 4 − d 111 X 2 1 − d 1 12 X 1 X 2 − d 122 X 2 2 − d 113 X 1 X 3 − d 114 X 1 X 4...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21
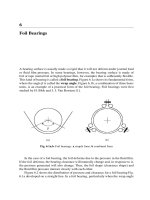
Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 8 docx
... x i 3 ) + 3 2 (h i+1 − h i )(h i x i+1 − h i+1 x i ) 2 (x i+1 2 − x i 2 ) +(h i x i+1 − h i+1 x i ) 3 (x i+1 − x i ) 1 −1 −11 (6 .21 ) V i = U (x i+1 − x i ) 2 1 2 (h i+1 − h i )(x i+1 2 − x i 2 ) +(h i x i+1 − ... − x 2 x 1 d 2 h dx 2 + p T − 1 R δhdx (6 .26 ) Equating this to zero gives the following stationary condition: δJ{h} = − x 2 x 1 d 2...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 9 pot
... z (7.35) I 2 − 2II =( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 ) + 2( xy 2 + yz 2 + zx 2 ) (7.36) Further, in cylindrical coordinates (r,θ,z), the strain invariant can be written as: I = r + θ + z (7.37) I 2 − 2II ... − ∂p ∂r + µ ∂ 2 r ∂r 2 + 1 r ∂ r ∂r + ∂ 2 r ∂z 2 − r r 2 (7.1) ρ ∂ z ∂t + r ∂ z ∂r + z ∂ z ∂z = − ∂p ∂z + µ ∂ 2 z ∂r 2 + 1 r ∂...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21

Hydrodynamic Lubrication 2009 Part 10 pps
... p ∂u ∂x + ∂ ∂y + ∂w ∂z + Φ (8. 42) where Φ = 2 ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ∂u ∂x 2 + ∂ ∂y 2 + ∂w ∂z 2 + 1 2 ∂u ∂y + ∂ ∂x 2 + 1 2 ∂ ∂z + ∂w ∂y 2 + 1 2 ∂w ∂x + ∂u ∂z 2 ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ + λ ∂u ∂x + ∂ ∂y + ∂w ∂z 2 (8.43) In ... constant: ρc DT Dt = ∂ ∂x k o ∂T ∂x + ∂ ∂y k o ∂T ∂y + ∂ ∂z k o ∂T ∂z + Φ (8.44) where Φ = 2 ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 08:21