Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 1 Part 10 pps
Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 1 Part 10 pps
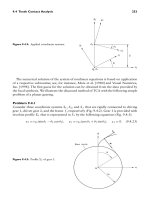
... 1 that is represented in S 1 by the following equations (Fig. 9.4.3): x 1 = r b1 (sin θ 1 − θ 1 cos θ 1 ), y 1 = r b1 (cos θ 1 + θ 1 sin θ 1 ), z 1 = 0. (9.4.23) Figure 9.4.3: Profile 1 of gear ... follows: m 12 = dφ 1 dφ 2 =− dθ 1 dθ 2 = r b2 r b1 . (9.4. 41) Step 7: The line of action is represented by the equation r (1) f = r b1 [ sin(θ 1 − φ 1 ) −...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 1 Part 9 pot
... a 22 : v (1) s a 11 + v (1) q a 12 = a 13 v (1) s a 12 + v (1) q a 22 = a 23 a 11 + a 22 = κ . (9.3 .11 ) Step 4: The solution of equation system (9.3 .11 ) for the unknowns a 11 , a 12 , and a 22 allows ... L ac v (12 ) t v (12 ) m = cos q 1 −sin q 1 sin q 1 cos q 1 v (12 ) t v (12 ) m (8.5.23) κ f = κ (1) t cos 2 q 1 − κ (1) m...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 6 ppsx
... Figs. 16 .2 .10 (a) and 16 .2 .10 (b) by functions Z 1 (γ, γ o ) and Z 1 (E,γ o ), Figure 16 .2 .10 : Illustration of variation of the shift Z 1 of the line of action due to errors (a) γ and (b) ... determined as follows: r (1) f (u 1 (ψ 1 ),ψ 1 ,φ 1 ) −r (2) f (u 2 ,ψ 2 ,φ 2 ) = 0 (16 .3.5) ∂r (1) f ∂ψ 1 · n (2) f = 0. (16 .3.6) Here, r (1) f (u 1 (ψ...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 7 pps
... r σ (u c ,θ c (u c ,ψ σ ),ψ σ ). (17 .4 .10 ) P1: JTH CB672 -16 CB672/Litvin CB672/Litvin-v2.cls February 27, 2004 0: 51 16.6 Stress Analysis 469 (Ave. Crit.: 75%) S, Pressure -8 .18 0e+ 01 +2.500e+ 01 +9.731e+ 01 +1. 696e+02 +2. 419 e+02 +3 .14 2e+02 +3.865e+02 +4.588e+02 +5. 311 e+02 +6.035e+02 +6.758e+02 +7.481e+02 +8.204e+02 +8.927e+02 1 2 3 (MPa) Figure ... velocities ω (1) and...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21
Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 8 pps
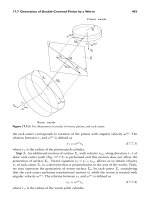
... rack-cutter a c = 0. 016 739 mm 1 , s a = 0.3m, parameter s 12 = 1. 0 [see Eq. (17 .3.2)], and module m = 1 mm. Functions h 1 (N 1 ) and h 2 (N 2 ) are obtained as discussed in Section 15 .8. 17 .10 STRESS ANALYSIS Stress ... s w )r w (u w ,θ w ) (17 .7 .10 ) N w · v (w1,ψ w ) w = 0 (17 .7 .11 ) N w · v (w1,s w ) w = 0. (17 .7 .12 ) P1: JXR CB672 -18 CB672/Litvin CB672/Litv...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 9 pps
... respectively, as r 1 (u 1 (φ 1 ),θ 1 (φ 1 )) (18 .13 .10 ) r 2 (u 2 (φ 1 ),θ 2 (φ 1 )). (18 .13 .11 ) Results of Investigation The results of investigation of the first version of geometry are represented in Fig. 18 .13 .3 ... S ∗ n to S 1 [Figs. 18 .10 .1( b) and 18 .10 .1( c)]. Step 2: Using the equation of meshing between the rack-cutter and the shaper, we obtain...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 10 doc
... the right-hand and left-hand worms and worm- gears by Eqs. (19 .2.8) and (19 .2.9), respectively. Equations (19 .2.8), (19 .2.9), (19 .3.9), and (19 .3 .10 ) yield m 21 = N 1 N 2 . (19 .3 .11 ) Shortest ... = 1 (19 .5 .17 ) where 1 = da 12 0 a 22 =∓ d cos δ sin µ sin λ p (19 .5 .18 ) = a 11 a 12 a 21 a 22 =∓ cos...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 3 ppsx
... r (b) p (λ f ,θ p ) ( 21. 4.8) where M 1p = M 1b 1 M b 1 a 1 M a 1 m 1 M m 1 c 1 M c 1 p M c 1 p = 10 0S r 1 cos q 1 010 S r 1 sin q 1 0 01 0 000 1 M m 1 c 1 = cos ... α p ( 21. 5 .14 ) and (Fig. 21. 4 .1) n (M) m 1 = L m 1 b 1 L b 1 1 n (M) 1 ( 21. 5 .15 ) where n (M) 1 ≡ n (M)...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 6 pps
... S 1 (x 1 , y 1 , z 1 ). Then, using the coordinate transformation from S 1 to S 1 (x 1 , y 1 , z 1 ), we will determine the normal N 1 and then obtain a 1 = N x1 i 1 + N z1 k 1 . ... SURFACES Step 1: Consider that the worm thread surface (say, the surface side I ) is represented by the vector equation (see Chapter 19 ) r 1 (u,θ) = x 1 (u,θ) i...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 2 Part 1 pot
... N c 2P . (11 .2 .14 ) (ii) It is obvious that E c (φ 2 ) − E (1) c E (2) c − E (1) c = φ 2 2πa . (11 .2 .15 ) (iii) Equations from (11 .2 .13 ) to (11 .2 .15 ) confirm Eq. (11 .2 .12 ). P1: JTH CB672 -11 CB672/Litvin ... from1upto20) b p = 1. 250 P − e p (10 .9.9) b g = 1. 250 P − e g (10 .9 .10 ) P1: FHA/JTH CB672 -10 CB672/Litvin CB672/Litvin-v2.cls February 27, 2004 0 :19 300 S...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21
- thiết kế bài giảng lịch sử 8 tập 1 part 3 ppsx
- tiếng anh giao tiếp new headway tập 1 part 10
- thiết kế bài giảng sinh học 11 nâng cao tập 1 part 6 pps
- võ thuật bắc phái tây sơn part 10 ppsx
- hóa học lập thể part 10 ppsx
- the prime minister and i episode 1
- law and order svu season 1 closure part 2
- prime minister and i episode 1 eng sub download