David G Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 3 pot

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 3 pot
... Self-scaling 1 20 0 .33 3 20 0 .33 3 20 0 .33 3 20 0 .33 3 2 2.7 32 7 89 93. 65457 93. 65457 2. 811061 33 836 899×10 2 56. 929 99 56. 929 99 3 5 627 69×10 2 46 37 6461×10 −4 1. 620 688 1. 620 688 4 20 0600 ×10 −4 51 21 9515×10 −5 5 25 1115×10 −1 5 25 1115×10 −1 4 726 918×10 −6 62 457944 ... ×10 −4 51 21 9515×10 −5 5 25 1115×10 −1 5 25 1115×10 −1 4 726 918×10 −6 62 457944 ×1...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 1 pot
... 34 198 02 6 31 3 36 19 3 42 9865 8 − 32 4 9978 3 42 9998 9 − 32 9 0408 34 30000 15 33 96 124 20 34 19 022 25 3 42 6004 30 3 42 83 72 35 3 42 927 5 40 3 42 9650 45 3 42 9 825 50 3 42 9909 55 − 3 42 9951 60 3 42 9971 Solution x ... −1446460 4 2 130 796 2 0 529 49 2 0 529 49 5 2 1 635 86 2 149690 2 06 0 23 4 6 2 17 027 2 2 1496 93 2 06 0 23 7 7 2 1 727 86 2 1679 83 2...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 5 potx
... problem minimize x 2 1 +x 2 2 +x 2 3 +x 2 4 −2x 1 −3x 4 subject to 2x 1 +x 2 +x 3 +4x 4 =7 (20 ) x 1 +x 2 +2x 3 +x 4 =6 x i 0i=1 2 3 4 Suppose that given the feasible point x = 2 2 1 0 we ... 14 73 ⎤ ⎦ and finally P = 1 11 ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ 1 31 0 39 30 1 31 0 0000 ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ (22 ) The gradient at the point (2, 2, 1, 0) is g = 2 4 2 3 and hence we find d =−Pg = 1...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 8 pot
... absolute-value penalty function. We minimize the function 2x 2 +2xy +y 2 −2y +cx (66) We rewrite (66) as 2x 2 +2xy +y 2 −2y +cx =2x 2 +2xy +cx+y −1 2 −1 =2x 2 +2x +cx+y −1 2 +2xy −1 ... charac- terization given here is a generalization of that in Luenberger [L10]. For the geometric inter- pretation, see Luenberger [L8]. The central path for nonlinear programm...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 10 potx
... programming expressed in Theorem 2, Section 5.6. 15.9 SEMIDEFINITE PROGRAMMING Semidefinite programming (SDP) is a natural extension of linear programming. In linear programming, the variables form a ... higher than the minimal objective cost. Example 2 (Linear Programming) . To see that the problem (SDP) (that is, (56)) generalizes linear programing define C = diagc 1 ...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 13 potx
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 1 Part 3 ppsx
... decreasing objective, the algorithm must reach a basis satisfying one of the two terminating conditions. Example 1. Maximize 3x 1 +x 2 +3x 3 subject to 2x 1 + x 2 + x 3 2 x 1 +2x 2 +3x 3 5 2x 1 +2x 2 + ... yields: 21 2104 33 10 13 r T −5 −4 30 0−7 First tableau Pivoting in the column having the most negative bottom row component as indicated, we obtain: 0 −1 4 /31 2/...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 1 Part 10 pot
... form x k+1 =x k − g T k g k g T k Qg k g k ( 32 ) where g k =Qx k −b. 21 8 Chapter 8 Basic Descent Methods N = 2 N = 3 N = 4 N = 5 4 4 5 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 8 1 5 1 3 2 3 1 2 2 5 3 5 2 8 3 8 5 8 Fig. ... −Ex k+1 Ex k = 2 g T k g k 2 g T k Qg k − g T k g k 2 g T k Qg k g T k Q −1 g k = g T k g k 2 g T k...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20
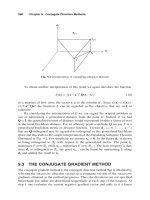
David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 2 ppt
... hypothesis both g k and Qd k belong to g 0 Qg 0 Q k+1 g 0 , the first by (a) and the second by (b). Thus g k+1 ∈ g 0 Qg 0 Q k+1 g 0 . Furthermore g k+1 g 0 Qg 0 Q k g 0 ... g 0 g 1 g k = g 0 Qg 0 Q k g 0 b) d 0 d 1 d k = g 0 Qg 0 Q k g 0 c) d T k Qd i =0 for i k −1 d) k =g T k g k /d T k Qd k...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20

David G. Luenberger, Yinyu Ye - Linear and Nonlinear Programming International Series Episode 2 Part 4 pps
... problem extremize x 1 +x 2 2 +x 2 x 3 +2x 2 3 subject to 1 2 x 2 1 +x 2 2 +x 2 3 =1 The first-order necessary conditions are 1+ x 1 =0 2x 2 +x 3 +x 2 =0 x 2 +4x 3 +x 3 =0 One solution to ... problem minimize 2x 2 1 +2x 1 x 2 +x 2 2 −10x 1 −10x 2 subject to x 2 1 +x 2 2 5 3x 1 +x 2 6 The first-order necessary conditions, in addition to...
Ngày tải lên: 06/08/2014, 15:20
- linear and nonlinear partial differential equations examples
- examples of linear and nonlinear differential equations
- examples of linear and nonlinear operators
- linear and nonlinear simultaneous equations calculator
- linear and nonlinear system
- linear and nonlinear simultaneous equation solver
- systems of linear and nonlinear equations worksheet
- linear and nonlinear differential equations ppt
- linear and nonlinear forward rates