Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P11 pot

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P11 pot
... Aronin N (1997) Aggregation of huntingtin in neuronal intranuclear inclusions and dystrophic neurites in brain. Science 277:1990–1993 Duyckaerts C, Potier MC, Delatour B (2008) Alzheimer disease ... of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18189–18194 Jones SR, Gainetdinov RR, Wightman RM, Caron MG (1998) Mechanisms of amphetamine action revealed in mice lacking the dopa...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20
Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P8 potx
... three or four tubulin-binding domains, Grey boxes: inserts from exon 2 near the N-terminus, Vertical lines in boxes: inserts from exon 3 near the N-terminus, and Black boxes: inserts from exon ... deposits in the parenchyma, indicating that BACE1 is in tight control of the balance in amyloid pathology in brain, promoting either parenchyma or vasculature. APP/ApoE Mice In epidemiol...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P10 pot
... is characterized by the following two important intracyto- plasmic inclusions: the Bunina bodies, which are small eosinophilic intraneuronal inclusions in the remaining lower motor neurons, are ... degeneration in the basal ganglia, periaqueducal gray, spinal cord, thalamus, and cerebral cortex. Brain regions showed positive staining for ubiquitin and α-synuclein, two proteins typically f...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P15 potx
... Brain Edema 133 6 Role of Aquaporins in Brain Edema 134 7 Injury Cascade in Brain Edema: Molecular Mechanisms 136 7.1 Cation Channels Involved in Cytotoxic Edema 137 7.2 Role of MMPs in the ... sulfate, and binding sites on the laminin and fibronectin molecules (Zlokovic, 2008). Within the basal lamina reside the pericytes (Fig. 1). Mesenchymal in origin, pericytes form an incom...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P16 pot
... including membranes, resulting in cell necrosis. In situations where the pH remains neutral, increases in intracellular cal- cium and cytokines cause induction of neutral proteases. The main neutral ... metabolic fail- ure is the main process resulting in cytotoxic edema. In addition to the injury occurring at the cell membrane, there are other molecular mechanisms involv- ing the...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P21 pot
... serotonin transporter: insights into the primary escitalopram-binding site. ChemMedChem 2:815–826 Monoamine Transporter Pathologies 185 7 Parkinson’s Disease (PD) Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized ... rigidity in movement, resting tremor, bradykinesia, and difficulty in maintaining postural stability (Gelb et al., 1999). PD is a neurodegenerative disease marked by Lewy bodies...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P26 potx
... Orientation in PD 256 6.2 Aging and Cognitive Event-Related Potentials 259 6.3 Neurotransmitters and Cognitive ERP-S in PD 259 6.4 Dopamine in Visual Processing in the Retina 260 6.5 Retinal Model ... emphasized in relation to visuocogntive and attentive dysfunction. The main neurotransmitter systems involved are dopamine (in PD) and acetyl- choline (both in PD and AD). The l...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P27 pot
... dysfunction. Affected retinal dopaminergic neurons do not have long projections. Recent imag- ing data, however, show neuronal thinning involving both inner nuclear layers and retinal ganglion cells. Retinal ganglion ... movement, followed by disinhibition of the same GPi and SNr neuron via input over the indirect pathway, thus inhibiting ongoing movement. In the alternative focusing model,...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P32 potx
... aligned according to ankyrin repeats. The amino-terminal signal response domain (SRD) and the carboxyl-terminal acidic region rich in prolines, glutamates, serines, and threonines (PEST) are indicated. ... neuronal death in various experimental models of neu- rodegenerative diseases. A potent inducer of NF-κB activation in astrocytes is bradykinin, an in ammatory mediator produced in...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20

Neurochemical Mechanisms in Disease P35 potx
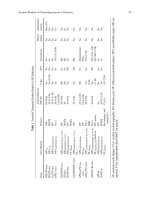
... Trinucleotide Expansion—Polyglutamine (Q n )-Expansion Diseases Ten CAG-expansion diseases are currently known. In nine of these diseases (listed in Table 2), the mutation occurs in an exon (coding region) and results in an ... findings suggest a toxic gain of function in the mutated SBMA. Androgens are important in regulating sexually dimorphic neurons in the rat brain. They are...
Ngày tải lên: 07/07/2014, 09:20