An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation 6 ppt

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_3 pptx
... rand and randn to generate U(0, 1) and N(0, 1) samples, respectively. To make the experiments reproducible, we set the random number generator seed to 100; that is, we used rand(‘state’,100) and ... sample means and variances approach the true values 0 and 1. A more enlightening approach to testing a random number generator is to divide the x-axis into subintervals, or bins,oflength...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_4 ppt
... known to investors, and hence any change in the price is due to new information. We may build this into our model by adding a ran- dom ‘fluctuation’ increment to the interest rate equation and making ... hand it can also be shown that, with probability 1, the path will not have a well-defined tangent at any point. 63 6. 7 Program of Chapter 6 and walkthrough 61 %CH 06 Program for C...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_5 ppt
... understand the factors that influence and move option prices butinthe absence of an ability to forecast these factors the transformation into money remains non-trivial. DILIP B. MADAN (Madan, 2001) Evidence ... able to transform this knowledge into money. Finance is consistent in its ability to build good models and consistent in its inability to make easy money. The purpose of the...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_8 pptx
... number generators to compute estimates of expected values was touched on in Chapter 4. Here we pull these two threads together and introduce the Monte Carlo approach to valuing an option. As we ... a and variance var(X) = b 2 are not known. Suppose • we are interested in computing an approximation to a (and possibly b), and • we are able to take independent samples of X using a...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation Mathematics Stochastics and Computation_9 ppt
... Exercise 19 .6. 19.5 Bermudan and shout options A Bermudan option differs from the corresponding American option in only one respect. While the American option allows the holder to exercise at any time ... t N j=1 S j 19 Exotic options OUTLINE • European-style options • path-dependent options: lookbacks, barriers and Asians • early exercise options: Bermudans and shouts • Monte Ca...
Ngày tải lên: 21/06/2014, 07:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_13 pot
... Von Neumann stability and convergence 247 0 5 10 15 0 2 4 6 8 10 0 0.2 0.4 0 .6 0.8 1 x BTCS: ν = 6. 6 t Fig. 23.7. BTCS solution on the heat equation (23.2), (23.3) and (23.4) with initial and boundary ... problem of valuing an American option can be couched in terms of a linear complementarity problem. It is possible to develop 24.2 FTCS, BTCS and Crank–Nicolson for Black–Scholes...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_14 pot
... G. and E. J. Stapleton (1998) Fast accurate binomial pricing of options. Finance and Stochastics, 2:3–17. Rogers, L. C. G. and O. Zane (1999) Saddle-point approximations to option prices. Annals ... 118 London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, 5, 135 London Stock Exchange, 50 Long-Term Capital Management, 93–94 lookback option, 191–192, 1 96 low discrepancy sequenc...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_1 pot
... MathWorks, Inc. AN INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL OPTION VALUATION Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation This is a lively textbook providing a solid introduction to financial option valuation for ... Finite difference grid relevant to binomial method. 263 24.2 Program of Chapter 24: ch24.m. 264 AN INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL OPTION VALUATION Mathematics, Stocha...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20
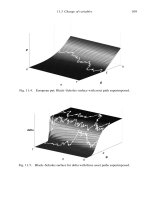
An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_7 pdf
... problem and it is marvelously intuitive. MARK P. KRITZMAN (Kritzman, 2000) To put it simply, if there is an arbitrage price, any other price is too dangerous to quote. MARTIN BAXTER AND ANDREW ... HOWISON AND JEFF DEWYNNE (Wilmott et al., 1995) Risk neutral valuation, which was developed by John Cox and Stephen Ross, has the dual virtues that it can be applied to practically any opt...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20

An Introduction to Financial Option Valuation: Mathematics, Stochastics and Computation_9 pot
... Chapter 8 that led to the Black–Scholes PDE can be adapted to cover an American put option. We write P Am (S, t) to denote the American put option value at asset price S and time t, and use (S(t)) ... log u d np and var log S(nδt) S 0 = log u d 2 np(1 − p). Hence, obtain ( 16. 5)–( 16. 6). 16. 3. Show that setting p = 1 2 in ( 16. 5)–( 16. 6) produces ( 16. 7...
Ngày tải lên: 20/06/2014, 18:20