methods of structural analysis

mathematical methods of engineering analysis - e. cinlar, r. vanderbei
... is open if and only if it is the union of a collection of open balls PROOF If A is the union of a collection of open balls, then A must be open in view of 8.2 and 8.3 To show the converse, let ... B be a bounded subset of a Euclidean space E Then, for every > there is a finite collection of closed balls of radius that covers B Here is the proof of Theorem 11.10 PROOF As mentioned above, ... Let E be the set of all sequences whose terms are the digits and Then, E is uncountable PROOF Let A be a countable subset of E Let x1 , x2 , be an enumeration of the elements of A, that is,...
Ngày tải lên: 31/03/2014, 15:21

MATRIX METHODS OF CIRCULAR ANALYSIS
... (23.87) Matrix methods of structural analysis 610 c = cosa s =sina A = cross-sectional area I = second moment of area of the element's cross-section I = elemental length E = Young's modulus of elasticity ... 12 - x 2 = 2kN 605 Matrix methods of structural analysis 606 From the figure above, at (c), the vector of generalised loads is obtained by considering the free degrees of freedom, which in this ... -1211~ -611~ 6112 1211~ 611’ 211 611‘ 411 - (23.84) Matrix methods of structural analysis 608 Now the stiffness matrix of equation (23.84) is of little use in that form, as most elements for a rigid-jointed...
Ngày tải lên: 08/04/2014, 11:28

methods of behavior analysis in neuroscience - jerry j. buccafusco
... Barbara Norwitz Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Methods of behavior analysis in neuroscience / edited by Jerry J Buccafusco p cm — (Methods and new frontiers of neuroscience) Includes ... the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center He holds the rank of Professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology and Professor of Psychiatry and Health Behavior Dr Buccafusco was trained classically ... at the Roche Institute of Molecular Biology under the direction of Dr Sydney Spector In 1979 he joined the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology of the Medical College of Georgia In 1989 Dr...
Ngày tải lên: 08/04/2014, 12:37

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P1 docx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member ... outlines the introduction of the two fundamental methods of structural analysis, the displacement method and the force method, and their applications to the two groups of structures, trusses and...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P2 doc
... are changed by the addition of one more diagonal member (9) Concluding remarks If the number of nodes is N and the number of constrained DOF is C, then (a) the number of simultaneous equations ... determined The resulting method of analysis is simple and straightforward and is very easy to be implemented into a computer program As a matter of fact, virtually all structural analysis computer packages ... Truss Analysis: Matrix Displacement Method by S T Mau Kinematic instability resulting from insufficient number of supports or members Problem 4: Discuss the kinematic stability of each of the...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 docx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member ... outlines the introduction of the two fundamental methods of structural analysis, the displacement method and the force method, and their applications to the two groups of structures, trusses and...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 pptx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member ... outlines the introduction of the two fundamental methods of structural analysis, the displacement method and the force method, and their applications to the two groups of structures, trusses and...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 2 pot
... are changed by the addition of one more diagonal member (9) Concluding remarks If the number of nodes is N and the number of constrained DOF is C, then (a) the number of simultaneous equations ... determined The resulting method of analysis is simple and straightforward and is very easy to be implemented into a computer program As a matter of fact, virtually all structural analysis computer packages ... given at the beginning of this section is obtained For example, the unconstrained global stiffness matrix component k34 is the superposition of (k34)1 of member and (k12)2 of member Note that the...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... direction of the FBD to the left or right of the cut 52 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau (2) Method of joint 16 kN Joints used to solve for vertical web member forces At each of the ... members of the second panel Σ Fx = (0.6)FCE + (0.6) FCG = Σ Fy = (0.8)FCE − (0.8) FCG = Example Discuss methods to find the force in the vertical web members of the K-truss shown 51 Truss Analysis: ... often leads to mistakes Example Find the member forces in bars 4, 5, 6, and of the loaded Fink truss shown 10 3 10 kN 3@2m=6m Fink truss to be solved by the method of joint 39 2m 11 1 Truss Analysis: ...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... direction of the FBD to the left or right of the cut 52 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau (2) Method of joint 16 kN Joints used to solve for vertical web member forces At each of the ... members of the second panel Σ Fx = (0.6)FCE + (0.6) FCG = Σ Fy = (0.8)FCE − (0.8) FCG = Example Discuss methods to find the force in the vertical web members of the K-truss shown 51 Truss Analysis: ... often leads to mistakes Example Find the member forces in bars 4, 5, 6, and of the loaded Fink truss shown 10 3 10 kN 3@2m=6m Fink truss to be solved by the method of joint 39 2m 11 1 Truss Analysis: ...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
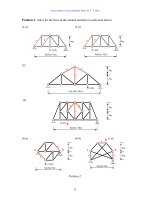
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pps
... Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Matrix Method of Joint The development of the method of joint and the method of section pre-dates the advent of electronic computer Although both methods ... deflection is the result of displacements of some or all of the truss nodes and nodal displacements are caused by the change of length of one or more members 2 3 Elongation of member induces nodal ... displacement method of analysis Since we are developing the force method of analysis herein, we shall not explore the application of this principle further at this point (3) Principle of Virtual Force...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
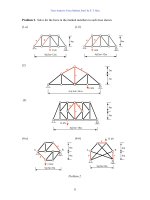
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pptx
... Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Matrix Method of Joint The development of the method of joint and the method of section pre-dates the advent of electronic computer Although both methods ... deflection is the result of displacements of some or all of the truss nodes and nodal displacements are caused by the change of length of one or more members 2 3 Elongation of member induces nodal ... displacement method of analysis Since we are developing the force method of analysis herein, we shall not explore the application of this principle further at this point (3) Principle of Virtual Force...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 5 pdf
... displacement of node of the loaded truss shown, given E=10 GPa, A=100 cm2 for all bars The magnitude of the pair of loads is 141.4 kN 1 2 3 4m 3@4m=12m Problem 5-2 (3) The lower chord members 1, 2, and of ... a counterclockwise rotation of 9.83mm/4,000mm=0.0025 radian 80 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part II by S.T.Mau Problem (1) Find the horizontal displacement of node of the loaded truss shown, ... rotation of bar 2, we note that the –9.83 computed represents a relative vertical movement between node and node of 9.83 mm in the opposite direction of what was assumed for the pair of unit loads...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 5 pps
... displacement of node of the loaded truss shown, given E=10 GPa, A=100 cm2 for all bars The magnitude of the pair of loads is 141.4 kN 1 2 3 4m 3@4m=12m Problem 5-2 (3) The lower chord members 1, 2, and of ... a counterclockwise rotation of 9.83mm/4,000mm=0.0025 radian 80 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part II by S.T.Mau Problem (1) Find the horizontal displacement of node of the loaded truss shown, ... rotation of bar 2, we note that the –9.83 computed represents a relative vertical movement between node and node of 9.83 mm in the opposite direction of what was assumed for the pair of unit loads...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
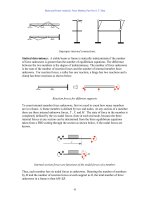
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 6 doc
... value of the load (4) According to Eq 2, the slope of the moment diagram is equal to the value of the shear, and the integration of the shear function gives the moment diagram 103 Beam and Frame Analysis: ... is an applied load (q≠0), the direction of change of the shear diagram follows the direction of the load and the rate of change is equal to the intensity of the load If a concentrated load is encountered, ... N=2, C=0 M=1, N=2, C=1 R=2 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =8, Number of equations = 3N+ΣC = Indeterminate to the 2nd degree R=1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =7, Number of equations = 3N+ΣC = Statically...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 6 pdf
... value of the load (4) According to Eq 2, the slope of the moment diagram is equal to the value of the shear, and the integration of the shear function gives the moment diagram 103 Beam and Frame Analysis: ... is an applied load (q≠0), the direction of change of the shear diagram follows the direction of the load and the rate of change is equal to the intensity of the load If a concentrated load is encountered, ... N=2, C=0 M=1, N=2, C=1 R=2 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =8, Number of equations = 3N+ΣC = Indeterminate to the 2nd degree R=1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =7, Number of equations = 3N+ΣC = Statically...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
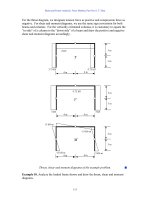
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 7 ppsx
... rotation of a section is equal to the rotation of the neutral axis The rate of change of angle of the neutral axis is defined as the curvature The reciprocal of the curvature is called the radius of ... The effect of shear deformation is the distortion of the shape of an element that results in the transverse deflections of a member The effect of flexural deformation is the bending of the element ... length-todepth ratio of a member is greater than ten, as a rule of thumb Consequently, the only effect to be included in the analysis of beam and frame deflection is that of the flexural deformation...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 8 ppsx
... Frame Analysis: Force Method, Part III Statically Indeterminate Beams and Frames When the number of force unknowns exceeds that of independent equilibrium equations, the force method of analysis ... and the method of solution is called the method of consistent deformations The procedures of the method of consistent deformations are outlined below (1) Determine the degree(s) of redundancy, ... combination of ∆b’ and Rbδbb is based on the concept of superposition, which states that the displacement of a linear structure due to two loads is the superposition of the displacement due to each of...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 9 pps
... Frame Analysis: Force Method, Part III by S T Mau The basic concept of the approximate methods is to assume the location of zero internal moments At the point of zero moment, the conditions of construction ... see from the previous examples, the force method of analysis for frames is practical for hand calculation only for cases of one to two degrees of redundancy Although we can computerize the process ... the formulation of the compatibility equation of the rigid frame shown EI is constant for all members P L L A rigid frame with three degrees of redundancy 166 Beam and Frame Analysis: Force Method,...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 1 ppsx
... are more than one DOF The above procedures for one DOF problem can still apply if we consider one DOF at a time That is to say that when we concentrate on one DOF, the other DOFs are considered ... Because of symmetry/anti-symmetry, we need to deal with only half of the span The other half is a mirror image of the first half in the case of symmetry and an upside down mirror image in the case of ... with a single degree of freedom (SDOF) Example Find all the member-end moments of the beam shown EI is constant for all members 30 kN-m a c b 5m 10 m Beam problem with a SDOF Solution (1) Preparation...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20