matrix methods of structural analysis

MATRIX METHODS OF CIRCULAR ANALYSIS
... the start of h s problem, X,O = 5 y," = 12.07 z30 = 0 Matrix methods of structural analysis 594 Substituting the above... + ($) (0.208 5 96 Matrix methods of structural analysis ... 23 Matrix methods of structural analvsis 23.1 Introduction This chapter describes and applies the matrix displacement method to various problems in structural analysis. The matrix ... m, y," = 5 m, Z,O = 0, zg0 = 7.07 (b) Front view of tripod m 592 Matrix. .. Front view of tripod m 592 Matrix methods of structural analysis Substituting the above into equation (23.56),
Ngày tải lên: 08/04/2014, 11:28

mathematical methods of engineering analysis - e. cinlar, r. vanderbei
... open if and only if it is the union of a collection of open balls PROOF If A is the union of a collection of open balls, then A must be open in view of 8.2 and 8.3 To show the converse, ... each of the following metrics: 1 d2 of Exercise 7.2 2 d1 of Exercise 7.2 3 d∞ of Exercise 7.2 4 d2 of Exercise 7.4 with w1 = 1 and w2 = 5 7.8 Open Balls in C For the metric space of ... introduce the idea of distance... uncountable PROOF Let A be a countable subset of E Let x1 , x2 , be an enumeration of the elements of A, that is, A is the range of (xn ) Note that
Ngày tải lên: 31/03/2014, 15:21

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 1 pdf
... are more than one DOF. The above procedures for one DOF problem can still apply if we consider one DOF at a time. That is to say that when we concentrate on one DOF, the other DOFs are considered ... illustrated in the following example of two DOFs. Example 2. Find all the member-end moments of the beam shown. EI is constant for all members. Example of a beam with two DOFs. Solution. (1) Preparation. ... procedures of the moment distribution method: (1) Identify the node which is free to rotate. In the present case, it was node b. The number of “free” rotating nodes is called the degree-of-freedom (DOF).
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 2 pptx
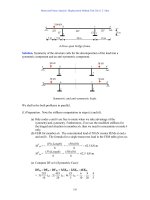
... by superposition of the standard model solutions as shown in the series of figures below. Beam and Frame Analysis: Displacement Method, Part I by S. T. Mau 203 Superposition of two standard models ... (7) Identify nodal rotations as degrees -of- freedom (DOFs) Identify nodal equilibrium in terms of member-end moments Express member-end moments in term of nodal rotation Solve for nodal rotation ... value of EK if we are interested only in the value of member-end moments The value of EK is needed only when we want to know the nodal rotation For problems with more than one DOF, we need
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 2 ppt
... by superposition of the standard model solutions as shown in the series of figures below. Beam and Frame Analysis: Displacement Method, Part I by S. T. Mau 203 Superposition of two standard models ... (7) Identify nodal rotations as degrees -of- freedom (DOFs) Identify nodal equilibrium in terms of member-end moments Express member-end moments in term of nodal rotation Solve for nodal rotation ... value of EK if we are interested only in the value of member-end moments The value of EK is needed only when we want to know the nodal rotation For problems with more than one DOF, we need
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 3 potx
... Treatment of side-sway. The end-nodes of a member may have translation displacements perpendicular to the axis of the member, creating a “rotation” like configuration of the member. This kind of displacement ... EI EI 2m 2m a a 2m 2m Problem 2 2 32 Beam and Frame Analysis: Displacement Method, Part II by S T Mau 4 Matrix Stiffness Analysis of. .. kN-m = −0. 82 kN-m From the member-end moments, ... at node b, there is another DOF, which is the horizontal displacement of node b or c, designated as ∆ as shown. Nodal lateral displacement that creates side-sway of memebr ab. Note that node
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 3 pps
... Treatment of side-sway. The end-nodes of a member may have translation displacements perpendicular to the axis of the member, creating a “rotation” like configuration of the member. This kind of displacement ... EI EI 2m 2m a a 2m 2m Problem 2 2 32 Beam and Frame Analysis: Displacement Method, Part II by S T Mau 4 Matrix Stiffness Analysis of. .. kN-m = −0. 82 kN-m From the member-end moments, ... at node b, there is another DOF, which is the horizontal displacement of node b or c, designated as ∆ as shown. Nodal lateral displacement that creates side-sway of memebr ab. Note that node
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 4 ppsx
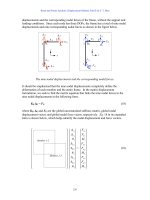
... corresponding to the DOFs of the first and the second nodes, while the contribution of member 2-3 will be associated with the DOFs at nodes 2 and 3. Before we assemble the global stiffness matrix, we need ... which is in the form of Eq. 22, with k G = Γ k L Γ T (26) Eq. 26 is the transformation formula of the member stiffness matrix. The expanded form of the member stiffness matrix in its explicit ... stiffness matrix In order to use the direct stiffness method to assemble the global stiffness matrix, we need the following table which gives the global DOF number corresponding to each local DOF of
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 4 doc
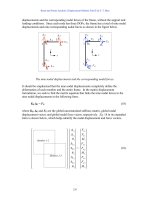
... corresponding to the DOFs of the first and the second nodes, while the contribution of member 2-3 will be associated with the DOFs at nodes 2 and 3. Before we assemble the global stiffness matrix, we need ... which is in the form of Eq. 22, with k G = Γ k L Γ T (26) Eq. 26 is the transformation formula of the member stiffness matrix. The expanded form of the member stiffness matrix in its explicit ... stiffness matrix In order to use the direct stiffness method to assemble the global stiffness matrix, we need the following table which gives the global DOF number corresponding to each local DOF of
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 2 Part 6 doc
... used in any displacement method of analysis. A sample of the numerical values of the factors in these two equations is given in the table below for two configurations of rectangular sections. The ... direct effect of temperature change and construction or manufacturing error is the change of shape or dimension of a structural member. For a statically determinate structure, this change of shape ... is linearly distributed from the bottom of a section to the top of the section and is constant along the length of the member. The strain at any level of the section can be computed as shown:
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

methods of behavior analysis in neuroscience - jerry j. buccafusco
... Barbara Norwitz Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Methods of behavior analysis in neuroscience / edited by Jerry J Buccafusco p cm — (Methods and new frontiers of neuroscience) Includes ... the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center He holds the rank of Professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology and Professor of Psychiatry and Health Behavior Dr Buccafusco was trained classically ... at the Roche Institute of Molecular Biology under the direction of Dr Sydney Spector In 1979 he joined the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology of the Medical College of Georgia In 1989 Dr...
Ngày tải lên: 08/04/2014, 12:37

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P1 docx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... that virtually all computer structural analysis programs are based on the matrix displacement method of analysis, the text begins with the matrix displacement method A matrix operations tutorial ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P2 doc
... are changed by the addition of one more diagonal member (9) Concluding remarks If the number of nodes is N and the number of constrained DOF is C, then (a) the number of simultaneous equations ... Truss Analysis: Matrix Displacement Method by S T Mau Kinematic instability resulting from insufficient number of supports or members Problem 4: Discuss the kinematic stability of each of the ... under any loading conditions 30 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I Introduction In the chapter on matrix displacement method of truss analysis, truss analysis is formulated with nodal displacement...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 docx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... that virtually all computer structural analysis programs are based on the matrix displacement method of analysis, the text begins with the matrix displacement method A matrix operations tutorial ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 pptx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... that virtually all computer structural analysis programs are based on the matrix displacement method of analysis, the text begins with the matrix displacement method A matrix operations tutorial ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, the second DOF of member...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 2 pot
... example, component (1,3) of the member-2 stiffness matrix is added to component (3,5) of the global stiffness matrix This simple way of assembling the global stiffness matrix is called the Direct ... dimension and member property given at the beginning of this section to arrive at the stiffness matrix for each of the three members: 16 Truss Analysis: Matrix Displacement Method by S T Mau ⎡ C2 ⎢ EA ... given at the beginning of this section is obtained For example, the unconstrained global stiffness matrix component k34 is the superposition of (k34)1 of member and (k12)2 of member Note that the...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
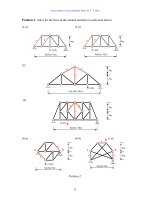
... direction of the FBD to the left or right of the cut 52 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau (2) Method of joint 16 kN Joints used to solve for vertical web member forces At each of the ... members of the second panel Σ Fx = (0.6)FCE + (0.6) FCG = Σ Fy = (0.8)FCE − (0.8) FCG = Example Discuss methods to find the force in the vertical web members of the K-truss shown 51 Truss Analysis: ... often leads to mistakes Example Find the member forces in bars 4, 5, 6, and of the loaded Fink truss shown 10 3 10 kN 3@2m=6m Fink truss to be solved by the method of joint 39 2m 11 1 Truss Analysis: ...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... direction of the FBD to the left or right of the cut 52 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau (2) Method of joint 16 kN Joints used to solve for vertical web member forces At each of the ... members of the second panel Σ Fx = (0.6)FCE + (0.6) FCG = Σ Fy = (0.8)FCE − (0.8) FCG = Example Discuss methods to find the force in the vertical web members of the K-truss shown 51 Truss Analysis: ... often leads to mistakes Example Find the member forces in bars 4, 5, 6, and of the loaded Fink truss shown 10 3 10 kN 3@2m=6m Fink truss to be solved by the method of joint 39 2m 11 1 Truss Analysis: ...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pps
... Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Matrix Method of Joint The development of the method of joint and the method of section pre-dates the advent of electronic computer Although both methods ... “inverse” of the matrix A, as apparent from Eq We can conclude: The nodal equilibrium conditions are completely characterized by the matrix A, the inverse of it, matrix F , is the force transfer matrix, ... deflection is the result of displacements of some or all of the truss nodes and nodal displacements are caused by the change of length of one or more members 2 3 Elongation of member induces nodal...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
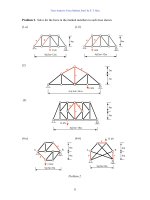
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pptx
... Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Matrix Method of Joint The development of the method of joint and the method of section pre-dates the advent of electronic computer Although both methods ... “inverse” of the matrix A, as apparent from Eq We can conclude: The nodal equilibrium conditions are completely characterized by the matrix A, the inverse of it, matrix F , is the force transfer matrix, ... deflection is the result of displacements of some or all of the truss nodes and nodal displacements are caused by the change of length of one or more members 2 3 Elongation of member induces nodal...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20