iii chapter iii obligations of the buyer articles 53 65

Đề tài " A stable trace formula III. Proof of the main theorems" pptx
... formula In the second paper [II], we established a key reduction in the proof of one of the global theorems In this paper, we shall complete the proof of the theorems We shall combine the global ... argument, the reader can consult the proof of Lemma 5.2 of [A2] and the discussion at the end of Section 10 of [AC].) The terms in the expansion therefore vanish The remaining distribution has ... a minor gap at the end of the argument in [AC, §2.17] We shall establish the global theorems in Section With the proof of Local Theorem in hand, we will see that the expansions of Sections 2–5...
Ngày tải lên: 05/03/2014, 23:20

Gián án Chapter 22 Chemistry of the Nonmetals
... Si in some of the lattice sites • SiO2 becomes AlO2− • the negative charge is countered by the inclusion of a cation Albite = ¼ of Si replaced by Al; Na(AlO2)(SiO2)3 Anorthite = ½ of Si replaced ... Forms of Carbon • coal is a mixture of hydrocarbons and carbon-rich particles the product of carbonation of ancient plant material carbonation removes H and O from organic compounds in the ... covalent atomic solids of Si and O and minor amounts of other elements found in rocks, soils, and clays silicates have variable structures – leading to the variety of properties found in rocks,...
Ngày tải lên: 28/11/2013, 01:12

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 12) ppt
... people of northern European descent Their diagnosis is obvious when they are visible as glittering particles upon the surface of the optic disc However, in many patients they are hidden beneath the ... fulminant papilledema Optic Disc Drusen These are refractile deposits within the substance of the optic nerve head (Fig 29-13) They are unrelated to drusen of the retina, which occur in age-related ... insidious fashion while the optic nerve develops atrophy In this setting, reduction of optic disc swelling is an ominous sign of a dying nerve rather than an encouraging indication of resolving papilledema...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 14) pps
... viewing light reflected from the fundus with an ophthalmoscope or by examining the dilated eye using the slit lamp The only treatment for cataract is surgical extraction of the opacified lens Over ... with chronic elevation of intraocular pressure In Americans of African descent it is the leading cause of blindness The mechanism whereby raised intraocular pressure injures the optic nerve is not ... In our litigious society, the fraudulent pursuit of recompense has spawned an epidemic of factitious visual loss Chronic Visual Loss Cataract This is a clouding of the lens sufficient to reduce...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 16) pps
... by administration of panretinal laser photocoagulation at the appropriate point in the evolution of the disease For further discussion of the manifestations and management of diabetic retinopathy, ... pigmentosa with black clumps of pigment in the retinal periphery known as "bone spicules." There is also atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, making the vasculature of the choroid easily visible ... deposits of clumped pigment in the peripheral retina, called bone spicules because of their vague resemblance to the spicules of cancellous bone, give the disease its name (Fig 29-17) The name...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 17) potx
... of retrobulbar fat, or fracture of the orbital floor The position of the eyes within the orbits is measured using a Hertel exophthalmometer, a hand-held instrument that records the position of ... be considered if the cause remains unknown after careful review of the history and thorough examination of the eye Figure 29-18 Proptosis When the globes appear asymmetric, the clinician must ... ophthalmopathy the tendons of the eye muscles are usually spared The Tolosa-Hunt syndrome may be regarded as an extension of orbital pseudotumor through the superior orbital fissure into the cavernous...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 18) ppt
... limitation of motility The width of the palpebral fissures is measured in primary gaze to quantitate the degree of ptosis The ptosis will be underestimated if the patient compensates by lifting the ... dehiscence or stretching of the aponeurotic tendon, which connects the levator muscle to the tarsal plate of the eyelid It occurs commonly in older patients, presumably from loss of connective tissue ... abnormal drooping of the eyelid Unilateral or bilateral ptosis can be congenital, from dysgenesis of the levator palpebrae superioris, or from abnormal insertion of its aponeurosis into the eyelid Acquired...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 19) ppsx
... affecting the innervation to either of the two muscles that open the eyelid: Müller's muscle or the levator palpebrae superioris Examination of the pupil helps to distinguish between these two ... (Diplopia) The first point to clarify is whether diplopia persists in either eye after covering the opposite eye If it does, the diagnosis is monocular diplopia The cause is usually intrinsic to the ... primary gaze, and then with the head turned and tilted in each direction In the above example, a cover test with the head turned to the right will maximize the fixation shift evoked by the cover test...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 20) ppt
... Occasionally, a catheter arteriogram must be done to exclude an aneurysm A lesion of the oculomotor nucleus in the rostral midbrain produces signs that differ from those caused by a lesion of the nerve ... itself There is bilateral ptosis because the levator muscle is innervated by a single central subnucleus There is also weakness of the contralateral superior rectus, because it is supplied by the ... space the oculomotor nerve is vulnerable to aneurysm, meningitis, tumor, infarction, and compression In cerebral herniation the nerve becomes trapped between the edge of the tentorium and the uncus...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 21) pps
... generation of saccades to the contralateral side After hemispheric stroke, the eyes usually deviate towards the lesioned side because of the unopposed action of the frontal eye field in the normal ... multiple sclerosis are the most common etiologies of brainstem abducens palsy After leaving the ventral pons, the abducens nerve runs forward along the clivus to pierce the dura at the petrous apex, ... Seizures generally have the opposite effect: the eyes deviate conjugately away from the irritative focus Parietal lesions disrupt smooth pursuit of targets moving toward the side of the lesion Bilateral...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 22) ppsx
... a combined lesion of the medial longitudinal fasciculus and the abducens nucleus on the same side The patient's only horizontal eye movement is abduction of the eye on the other side Figure 29-19 ... controlled at the level of the midbrain The neuronal circuits affected in disorders of vertical gaze are not fully elucidated, but lesions of the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal ... position of gaze the eyes appear normal B Horizontal gaze to the left is intact C On attempted horizontal gaze to the right, the left eye fails to adduct In mildly affected patients the eye may...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 23) pptx
... examination of the eyes Observation of nystagmoid movements of the optic disc on ophthalmoscopy is a sensitive way to detect subtle nystagmus Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus This is the most common form of jerk ... lesions, the nystagmus does not appear until several months of age Congenital motor nystagmus, which looks similar to congenital sensory nystagmus, develops in the absence of any abnormality of the ... be oblivious to their nystagmus Others will complain of blurred vision, or a subjective, to-and-fro movement of the environment (oscillopsia) corresponding to their nystagmus Fine nystagmus may...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 8) ppsx
... judicious use of topical glucocorticoids Dilation of the pupil reduces pain and prevents the formation of synechiae Posterior Uveitis This is diagnosed by observing inflammation of the vitreous, ... If these agents fail, topical or even systemic glucocorticoid therapy may be necessary, especially if an underlying autoimmune process is active Uveitis Involving the anterior structures of the ... disease Some patients have panuveitis, or inflammation of both the anterior and posterior segments of the eye Posterior uveitis is a manifestation of autoimmune diseases such as sarcoidosis, Behçet's...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 9) potx
... Ophthalmoscopy reveals zones of whitened, edematous retina following the distribution of branch retinal arterioles Complete occlusion of the central retinal artery produces arrest of blood flow and a ... term refers to a transient ischemic attack of the retina (Chap 364) Because neural tissue has a high rate of metabolism, interruption of blood flow to the retina for more than a few seconds results ... (Fig 29-6) Emboli are composed of either cholesterol (Hollenhorst plaque), calcium, or platelet-fibrin debris The most common source is an atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid artery or aorta,...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21
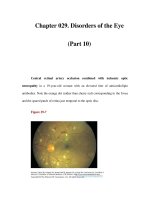
Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 10) potx
... confirm the diagnosis Glucocorticoids should be started immediately, without waiting for the biopsy to be completed The diagnosis of arteritic AION is difficult to sustain in the face of a negative ... spontaneously, while others evolve a frank obstruction with extensive retinal bleeding ("blood and thunder" appearance), infarction, and visual loss Venous occlusion of the retina is often idiopathic, ... through the posterior ciliary arteries supplying the optic disc It produces painless, monocular visual loss that is usually sudden, although some patients have progressive worsening The optic...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 11) potx
... of acute optic disc edema Many agents have been implicated as a cause of toxic optic neuropathy, but the evidence supporting the association for many is weak The following is a partial list of ... (measured months after the attack), but the recovery of visual function occurs more rapidly For some patients, optic neuritis remains an isolated event However, the ONTT showed that the 10-year cumulative ... hence the rubric, "the doctor sees nothing, and the patient sees nothing." Optic atrophy develops after severe or repeated attacks Virtually all patients experience a gradual recovery of vision...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 1) doc
... error with the excimer laser by performing LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) to alter the curvature of the cornea With the onset of middle age, presbyopia develops as the lens within the eye ... by input to the pretectal olivary nuclei in the midbrain The pretectal nuclei send their output to the Edinger-Westphal nuclei, which in turn provide parasympathetic innervation to the iris sphincter ... diverging lens in front of the eye In hyperopia, the globe is too short, and hence a converging lens is used to supplement the refractive power of the eye In astigmatism, the corneal surface is...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21

Chapter 029. Disorders of the Eye (Part 3) pptx
... front of the patient at about m If the eyes are straight, the corneal light reflex will be centered in the middle of each pupil To test eye alignment more precisely, the cover test is useful The ... uncovered and the test is repeated on the second eye If neither eye moves, the eyes are aligned orthotropically If the eyes are orthotropic in primary gaze but the patient complains of diplopia, the cover ... arteritis) After denervation of the iris sphincter the pupil does not respond well to light, but the response to near is often relatively intact When the near stimulus is removed, the pupil redilates...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 15:21