how orthodontic appliances move teeth

HOW WOULD YOU MOVE MOUNT FUJI
... Poundstone's HOW WOULD YOU MOVE MOUNT FUJI? "Combines how- to with be-smart for an audience of job seekers, interviewers, Wired-style cognitive science hobbyists, and the onlooking curious How Would ... manages to sneak in a wealth of material on the crucial issue of how to hire in today's knowledge-based economy How Would You Move Mount Fuji? delivers on the promise of revealing the tricks ... accomplished science journalist, shows how puzzles can — and cannot — identify the potential stars of a competitive company Poundstone gives smart advice to candidates on how to 'pass' the puzzle game...
Ngày tải lên: 15/10/2013, 23:13

sensing intelligence motion how robots humans move vladimir j lumelsky pptx
... planning, or the Piano Mover’s model The symbolism behind the latter term is that when movers set out to move a piano, they can first sit down and figure out the whole sequence of moves and turns and ... gentle in how they “mind” their movement.1 A nonprofessional reader curious about the possibilities of intelligent robots will find long layman-level passages in Sharp “robot-like” movements have ... almost like designing a friend One day you move your hand in a stroking movement along the robot’s skin, and it responds with a gentle appreciative movement This gives you a strange feeling:...
Ngày tải lên: 27/06/2014, 18:20

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... planning, or the Piano Mover’s model The symbolism behind the latter term is that when movers set out to move a piano, they can first sit down and figure out the whole sequence of moves and turns and ... gentle in how they “mind” their movement.1 A nonprofessional reader curious about the possibilities of intelligent robots will find long layman-level passages in Sharp “robot-like” movements have ... almost like designing a friend One day you move your hand in a stroking movement along the robot’s skin, and it responds with a gentle appreciative movement This gives you a strange feeling:...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... choreographer physically moves a dancer’s arm through the air, “That’s how you it.” For example, in preparation for a robot painting of a car body, an experienced human painter moves the arm with the ... unstructured world There are obvious examples showing what this can give We would not doubt, for example, that, other issues aside, a robot can move a scalpel inside a patient’s skull with more ... for “complete knowledge” when moving around, it is not obvious how big that knowledge can be even in simple cases For example, to move in a room, the database will have to include literally every...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... example in Figure 2.9, such a controller would work as long as the arm moves in free space But when the arm attempts to move its endpoint along the surface of table T , a contact constraint comes ... own complications; for example, each can be built as a PID controller shown in Figure 2.8.) Remember that the controller shown in Figure 2.10 can provide a successful compliance control only specifically ... controller − fx fy Figure 2.10 In the task shown in Figure 2.9, this compliance control scheme will provide position control during the motion between the positions shown in Figures 2.9a and 2.9c and will...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 4 pptx
... skills include three actions: It knows how to move toward point T on a straight line, how to move along the obstacle boundary, and how to start moving and how to stop The only input information ... path planning algorithm satisfying the assumptions of our model, any (however large) P > 0, any (however small) D > 0, and any (however small) δ > 0, there exists a scene in which the algorithm will ... described by Abelson and diSessa [36] The algorithm is shown to converge; no performance bounds are given (its performance was assessed later in Ref 56) However, the algorithm addresses a problem different...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 5 pptx
... Algorithmic Ideas To understand how vision sensing can be incorporated in the algorithms, consider first how the “pure” basic algorithm Bug2 would behave in the scene shown in Figure 3.12 Assuming ... its choice will somehow relate to the robot’s global goal In the algorithms, every Ti will lie on the M-line or on an obstacle boundary For a path segment whose point Ti moves along the M-line, ... either of the two classes can better than Bug1 104 MOTION PLANNING FOR A MOBILE ROBOT How much variety and how many algorithms are there in Classes and 2? For Class 1, the answer is simple: At...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 6 pot
... first move along the parabola defined by control p = −pmax toward ˆ curve (4.2), and then with control p = pmax move along the curve to the origin If ˆ point (V0 , x0 ) is below the switch curve, move ... obstacle, in order to immediately initiate a stopping path, move back to Ci , and then move directly toward Ti This would be quite inefficient, however Instead, the procedure operates as follows: Once ... compared to the robot, or if obstacles move more or less in one place, like a tree in the wind, then the robot will likely get where it intends Even if obstacles move faster than the robot, but their...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
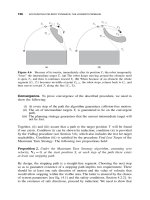
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
... two-link arms shown in Figure 5.1 can be arranged in more kinematic arrangements, and hence more geometries, beyond those shown in the figure Note, for example, that in the RR arm planar arm shown in ... Maximum Turn Strategy in a computer simulated environment Generated paths are shown by thicker lines For comparison, also shown by thin lines are paths produced under the same conditions by the VisBug ... example shown in Figure 4.1, note that if the robot walked under a kinematic algorithm, at point P it would make a sharp turn (recall that the algorithm assumes holonomic motion) In our case, however,...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 8 doc
... type shown in Figure 5.8c Figures 5.3 and 5.6 provide examples of the Type I case of Figure 5.8a An example for the Type II case in Figure 5.8b is shown in Figure 5.7 The Type II case shown in ... closed curve (in order not to complicate the picture, it is not shown in Figure 5.7a) The image of the corresponding virtual obstacle is shown in Figure 5.7b As one can see, the virtual boundary forms ... workspace Simple examples will show that paths produced by the arm endpoint when moving around even simple obstacles are complex and self-intersecting We will also see, however, that the said property...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
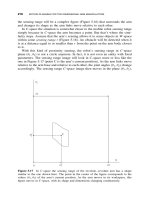
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
... the arm’s endpoint moves in the plane (b) This arm’s endpoint moves on the surface of a sphere (c) This arm’s endpoint moves on the surface of a torus (d) This arm’s endpoint moves on the surface ... is shown in Figure 5.1d An example of the arm’s interaction with two circular obstacles is shown in Figure 5.25a C-space images of the corresponding virtual obstacles and of the M-line are shown ... configurations We will review here those configurations, as an example of how such variability occurs as well as to see how the theory developed above applies to them This exercise also helps train...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 10 doc
... or when the robot can move between two obstacles only by simultaneously touching them both (Figure 5.33) We will show in Section 5.8.3 that after these situations are removed, CSO presents a ... robot, it must be possible for the robot to move in the direction of the force if the object were removed With this definition of a contact, the robot shown in Figure 5.34 is not in contact with ... trivial and cannot be simply assumed It has been shown in Ref 109 that in general CSO boundaries are not manifolds Consider, for example, the example shown in Figure 5.33a The setting is such that...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 11 docx
... effector in W -space, the paths are shown in C-space only Example The arm’s workspace contains only two obstacles, O2 and O3 , of those three shown in Figure 6.2 Shown in Figure 6.11 are the corresponding ... show that C-obstacles formed by interaction between link l2 and obstacles always extend in C-space in the direction of one semi-axis of link l2 and both semi-axes of link l3 ; it will also show ... contacting obstacles Here the C-point can choose either to move along the intersection curve between the plane and one of the obstacles, or move along the intersection curve between the two obstacles...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 12 pdf
... three physical obstacles O1 , O2 , and O3 shown in Figure 6.15a produce the robot workspace shown in Figure 6.15b and produce the configuration space shown in Figure 6.15c Notice that the Type ... then the robot moves directly toward jt Along this path segment the robot will either reach jt or encounter an obstacle, in which case the target is not reachable This shows how a motion planning ... is, however, that the sum of this knowledge tells us only what those human strategies might be, not what they are Whatever those unknown strategies that humans use to move around, we can, however,...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 13 docx
... quite common in industrial and other manipulators.) And, of course, the arm moves only in the plane of the screen How does one control the arm motion in this setup? By positioning the cursor ... mechanism, they just see that the arm moves as they expect.) This second option allows one to control both links motion simultaneously It is as if someone moves your hand on the table—your arm ... view: One has a complete view of the arm and the obstacles, as shown in Figure 7.5 Imagine you are that subject You are asked to move the arm, collision-free, from its starting position S to the...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 14 docx
... subject is, in general, independent of how quickly or slowly DISCUSSION 385 one moves the arm or how continuous its motion is If the subject stops to think how to proceed, this in itself will not ... the sensitive skin is shown in Figure 8.1; in the figure, software blocks are shown by straight rectangles, and hardware items are shown by curved rectangles As the robot moves in the course of ... seems to be no right age for learning how to move kinematic structures Then, we may want to delegate this job to robots, especially if robots can it better, as shown in prior chapters The results...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21