Fundamentals of structural dynamics


Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P1 docx
... have a direct bearing on the design of the content of a course in structural analysis: the reduction of credit hours to three required hours in structural analysis in most civil engineering curricula ... four DOFs, since each node has two DOFs and there are two nodes for each member We may also use the way each of the DOF is sequenced to refer to a particular DOF For example, t...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis P2 doc
... are changed by the addition of one more diagonal member (9) Concluding remarks If the number of nodes is N and the number of constrained DOF is C, then (a) the number of simultaneous equations ... determined The resulting method of analysis is simple and straightforward and is very easy to be implemented into a computer program As a matter of fact, virtually all structural an...
Ngày tải lên: 06/07/2014, 11:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 docx
... from each of the three nodes NODE FBD Py2 (Fx2 )1+ (Fx2)2 Px2 (Fy2 )1+ (Fy2)2 (Fy2 )1 (Fy2)2 2 (Fy1 )1 (Fy3)2 (Fx1 )1 (Fx3)2 3 Py1 (Fx1 )1+ (Fx1)3 (Fx2)2 (Fx2 )1 Px1 (Fy1 )1+ (Fy1)3 (Fy1)3 (Fx1)3 Py3 (Fx3)2+ ... 93 94 10 1 10 2 10 9 11 8 Beam and Frame Analysis: Force Method, Part II Deflection of Beam and Frames Problem 12 1 12 1 13 2 iii Problem Problem 14 3 15 2 Beam an...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 1 pptx
... from each of the three nodes NODE FBD Py2 (Fx2 )1+ (Fx2)2 Px2 (Fy2 )1+ (Fy2)2 (Fy2 )1 (Fy2)2 2 (Fy1 )1 (Fy3)2 (Fx1 )1 (Fx3)2 3 Py1 (Fx1 )1+ (Fx1)3 (Fx2)2 (Fx2 )1 Px1 (Fy1 )1+ (Fy1)3 (Fy1)3 (Fx1)3 Py3 (Fx3)2+ ... 93 94 10 1 10 2 10 9 11 8 Beam and Frame Analysis: Force Method, Part II Deflection of Beam and Frames Problem 12 1 12 1 13 2 iii Problem Problem 14 3 15 2 Beam an...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 2 pot
... 31 ⎪ ⎪ ⎢ ⎪ Fy ⎪ ⎢k 41 ⎩ ⎭ ⎣ 0 0 0 k 11 k 21 k 31 k 41 k 12 k 22 k 32 k 42 k13 k 23 k 33 k 43 0 0 0 k13 k 23 0 k 12 k 22 0 k 32 k 42 0 0 0 k 33 k 43 ⎤ ⎧u1 ⎫ ⎥ ⎪ v1 ⎪ ⎥ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ k14 ⎥ ⎪u ⎪ ⎥ ⎨ ⎬ k 24 ... equation: ⎡ K 11 ⎢K ⎢ 21 ⎢ K 31 ⎢ ⎢ K 41 ⎢ K 51 ⎢ ⎢ K 61 ⎣ K 12 K 22 K 32 K 42 K 52 K 62 K 13 K 23 K 33 K 43 K 53 K 63 K 14 K 24 K 34 K 44 K 54 K 64 K 15 K 25...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... (2-c) kN 1. 5m kN kN 3m 3m 3m 2m 4m 4m (3- a) (3- b) 1. 2 m kN 4kN 5kN kN 1. 6 m (4-a) 0.7 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 0.7 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 2m (3- c) 1. 2 m 1. 2 m 3m 3m (4-b) (4-c) kN kN 2m 2m kN 1m 1m 1m 1m 2m 2m ... Fy = 0, F5 (3/ 5) – F4 (3/ 5) –F1= 0, F1= –6 kN 38 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Joint Σ Fx = 0, 4 F6(4/5) + F3(4/5) =0, F3 = kN Σ Fy = 0, F6 F6 (3/ 5) – F3 (3/...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 3 pps
... (2-c) kN 1. 5m kN kN 3m 3m 3m 2m 4m 4m (3- a) (3- b) 1. 2 m kN 4kN 5kN kN 1. 6 m (4-a) 0.7 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 0.7 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 0.9 m 2m (3- c) 1. 2 m 1. 2 m 3m 3m (4-b) (4-c) kN kN 2m 2m kN 1m 1m 1m 1m 2m 2m ... Fy = 0, F5 (3/ 5) – F4 (3/ 5) –F1= 0, F1= –6 kN 38 Truss Analysis: Force Method, Part I by S T Mau Joint Σ Fx = 0, 4 F6(4/5) + F3(4/5) =0, F3 = kN Σ Fy = 0, F6 F6 (3/ 5) – F3 (3/...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
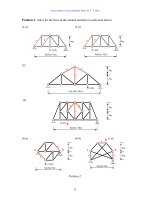
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pps
... Denoting the elongation of memebr as V3 We have (a) V3= α (∆T)L= 1. 2 (10 -5)/oC ( 14 oC) (6,000 mm)= 1mm (b) V3=1mm (c) V3= 16 kN (6 m)/[200 (10 6) kN/m2 (500) (10 -6)m2]=0.0 01 m= 1mm Next we need to find ... Example 11 only in the externally applied loads Use the force transfer matrix of Eq to find the solution 1. 0 kN 0.5 kN y x 4m 3 3m 3m Problem 4- 2 66 1. 0 kN Truss Analysi...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
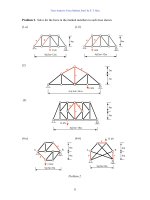
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 4 pptx
... Denoting the elongation of memebr as V3 We have (a) V3= α (∆T)L= 1. 2 (10 -5)/oC ( 14 oC) (6,000 mm)= 1mm (b) V3=1mm (c) V3= 16 kN (6 m)/[200 (10 6) kN/m2 (500) (10 -6)m2]=0.0 01 m= 1mm Next we need to find ... Example 11 only in the externally applied loads Use the force transfer matrix of Eq to find the solution 1. 0 kN 0.5 kN y x 4m 3 3m 3m Problem 4- 2 66 1. 0 kN Truss Analysi...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 5 pdf
... -56 .56 40.00 -56 .56 -40.00 25, 000 25, 000 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 3.20 3.20 1. 60 -6.40 4.80 -3.20 1. 60 -3.20 -1. 60 0.00 -0. 71 0.00 0.00 -0. 71 1.00 -0. 71 0.00 -0. 71 -0.33 -0.33 ... -0.8 -0.032 0.026 0 .50 33,333 0. 0 15 -0.6 -0.009 -0. 018 0. 011 -0.83 20,000 -0.042 1. 0 -0.042 0. 050 0. 050 20,000 1. 0 0. 050 0. 050 (kN/m) Vι (mm) -0.33 25,...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 5 pps
... -56 .56 40.00 -56 .56 -40.00 25, 000 25, 000 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 17 ,680 25, 000 3.20 3.20 1. 60 -6.40 4.80 -3.20 1. 60 -3.20 -1. 60 0.00 -0. 71 0.00 0.00 -0. 71 1.00 -0. 71 0.00 -0. 71 -0.33 -0.33 ... -0.8 -0.032 0.026 0 .50 33,333 0. 0 15 -0.6 -0.009 -0. 018 0. 011 -0.83 20,000 -0.042 1. 0 -0.042 0. 050 0. 050 20,000 1. 0 0. 050 0. 050 (kN/m) Vι (mm) -0.33 25,...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
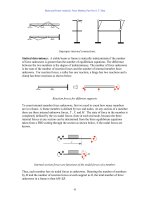
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 6 doc
... M=2, N=3, C =1 R =1 R =1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =12 , Number of equations = 3N+ΣC= 11 Indeterminate to the 1st degree Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =10 , Number of equations = 3N+C= 10 Statically ... M=5, N =6, C=2 M=3, N=4, C =1 R=3 R=2 R=3 R=3 R=2 R =1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR = 21, Number of equations = 3N+C = 20 Indeterminate to the 1st degree Number of unknowns 3M...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis Episode 1 Part 6 pdf
... M=2, N=3, C =1 R =1 R =1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =12 , Number of equations = 3N+ΣC= 11 Indeterminate to the 1st degree Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR =10 , Number of equations = 3N+C= 10 Statically ... M=5, N =6, C=2 M=3, N=4, C =1 R=3 R=2 R=3 R=3 R=2 R =1 Number of unknowns = 3M+ΣR = 21, Number of equations = 3N+C = 20 Indeterminate to the 1st degree Number of unknowns 3M...
Ngày tải lên: 05/08/2014, 09:20
- coarse molecular dynamics analysis of structural transitions in solid materials
- fundamentals of electric circuits
- the fundamentals of reverse osmosis
- fundamentals of machine components
- fundamentals of machine component design
- the fundamentals of success
- the use of structural steel in building
- fundamentals of chinese language processing