Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 6 ppt

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 6 ppt
... " 1 Fig. 6. 29. Schematic illustration of the tem- p e rature dependence of the yield strength of face-centred and body-centred cubic metals Here k is Boltzmann’s constant and T the absolute ... 10). Table 6. 6 summarises the strength of some particle-strengthened alu- minium alloys. Precipitation hardening Strengthening of materials by fine particles is frequently obtai...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 7 pptx
... expansion of the two materials, the matrix is stressed compressively near the particles, impeding crack propa- 262 8 Mechanical behaviour of polymers T degree of polymerisation 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 T m T g viscous ... for viscoplastic behaviour only. 260 8 Mechanical behaviour of polymers 1/% T T g free volume Fig. 8.3. Specific vol ume 1/ of an amo...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 10 pptx
... glass 40 % C Fig. 10.25. Comparison of the S-N curves of unreinforced as well as glass- and carb on-reinforced polysul fone (simplified plot after [29]) S-N curves of fibre composites According to section ... causing ratchetting. ∗ 10 .6. 6 Ki tagawa diagram In sections 10 .6. 1 and 10 .6. 2, we discussed two different ways to design with cyclically loaded materials. Using fracture...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 11 pptx
... Creep deformation In section 8.2.1, the time-dependent behaviour of polymers was described using spring -and- dashpot models. a) Sketch a spring -and- dashpot model suitable to describe creep deformation! b) ... Larson-Miller data R m/100 000/T /MPa temp e rature in ℃ 420 450 500 550 60 0 700 800 900 ferritic steels C 35 108 69 34 19 Mn 5 1 36 85 41 24 CrMo 5 308 2 26 118 36 10 CrM...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 2 doc
... and semi-metals Al 70 64 76 1.23 108 61 29 Au 78 43 117 1.89 1 86 157 42 Cu 121 67 192 3.22 168 121 75 α-Fe 209 129 2 76 2.13 233 124 117 Ni 207 137 305 2.50 247 147 125 Si − 130 188 1.57 166 64 ... E isotr. C 11 C 33 C 44 C 12 C 13 GPa GPa GPa GPa GPa GPa Mg 44 60 62 16 26 22 Ti 112 162 181 47 92 69 Zn 103 164 64 39 36 53 ∗ 2.4.7 Other crystal lattices The number of indepe...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 4 docx
... stress-s train curve of AlSi 1 MgMn from figure 4 .6. Taking the value of σ nss = 188 .6 MPa and Young’s modulus of E = 66 200 MPa, we find from equation (4.5) σ max × ε max = (188 .6 MPa) 2 66 200 ... between the particles, the matrix is only single-phase and thus has an increased ductility. The cavities thus grow by slipping of the matrix (see sections 6. 2.3 and 6. 2.5) o...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 5 doc
... 2110 6 1 6 Ti, Mg, Zr {0112} 2110 6 1 6 Zn {1122} 1100 6 1 6 Ti Burgers vector out of basal plane {0110} 2113 3 2 6 Zn {0111} 2113 6 2 12 Zr {1121} 2113 6 2 12 Zn, Zr {1122} 2113 6 2 ... understanding of dislocations. 6. 2 Dislocations 6. 2.1 Typ es of dislocations Dislocations are one-dimensional (line-s haped ) lattice defec ts. Figure 6. 2(a) show...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20

Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 8 pot
... Araneus diadematus and 8.4 Plastic behaviour 275 Table 8.1. Cross-linking density and Young’s modulus of different types of polymers (cf. section 1.4.2) type of material cross-linking density E/GPa thermoplastics ... chain molecules is larger and enables 9 Mechanical behaviour of fibre reinforced composites In composites, different materials are combined to exploit fav...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20
Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Metals, Ceramics, Polymers and Composites 2010 Part 9 pot
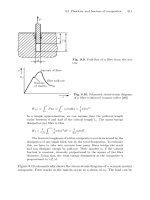
... application of ceramic matrix composites are cutting tools made of SiC-whisker reinforced aluminium oxide for cutting of hard-to-machine materials, especially nickel- base superalloys and hardened ... enamel. 314 9 Mechanical behaviour of fibre reinforced composites ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ Fig. 9.11. Deformation of a fibre composite under compressive stress. The fibres can b end in an in-ph...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 15:20