Introduction to Elasticity Part 15 pot

Introduction to Elasticity Part 15 pot
... vector can therefore be written equivalently as u 1 ,u 2 ,u 3 . A common and useful shorthand is simply to write the displacement vector as u i ,wherethe isubscript is an index that is assumed to ... grain size E modulus of elasticity, electric field E ∗ activation energy E viscoelastic stiffness operator e electronic charge e ij deviatoric strain F force f s form factor for shear G shear...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 5 pot
... pseudovector form. This relation serves to define the stress concept as an entity that relates the traction (a vector) acting on an arbitrary surface to the orientation of the surface (another vector). ... equation. (c) Determine the principal stresses. 15 which causes the principal planes to appear at ±45 ◦ to the chalk’s long axis. The crack will appear transverse to the principa...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

The Oxford Companion to Philosophy Part 15 pot
... continued to adhere to a fundamentally empiricist theory of meaning which required scientific hypotheses to be susceptible to empirical confirmation. He also, in consequence, adhered to the *analytic–synthetic ... George Brett and later Fulton H. Anderson shaped the philosophy depart- ment at the University of Toronto into one of the fore- most places for the study of the history of p...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 1 docx
... from its top; we obtained L =15. 6km. Were such a rod to be constructed, our analysis predicts the deformation at the bottom would be δ = γL 2 2E = 7.85 × 10 3 (kg/m 3 ) × 9.8(m/s 2 ) × [15. 6 × ... the loads to be applied to the structure are known at the outset, and we wish to compute how much material will be needed to support them. As a very simple case, let’s say we wish to u...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 2 docx
... stretches to λ d , after which the engineering stress there would have to rise to stretch it further. But this stress is greater than that needed to stretch material at the edge of the neck from λ Y to ... material, but it is also possible to arrange for them to be oriented preferentially in the direction expected to have the highest stresses. Such a material is said to be a...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 4 ppt
... force vector F: T = r × F (6) This vector is in a direction given by the right hand rule, and is normal to the plane containing the point O and the force vector. The torque tending to loosen ... cross-sectional dimension b × h, are to be glued together using a tongue-and-groove joint as shown in Fig. 3, and we wish to estimate the depth d of the glue joint so as to make the joint ap...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:20

Introduction to Elasticity Part 6 pps
... = x y z γ yz γ xz γ xy = 0.01 0.02 0.0 0.0 0 .15 0.0 4. Given the stress tensor σ ij = 123 245 357 (MPa) (a) Dissociate σ ij into deviatoric and dilatational parts Σ ij and (1/3)σ kk δ ij . 9 For ... said to be orthotropic. 6 Constitutive...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21
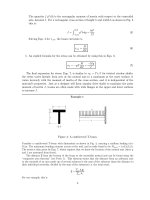
Introduction to Elasticity Part 7 pdf
... radius r 1 to r 2 over the length L. We wish to determine the deflection caused by a force F applied to the free end of the beam, at an angle θ from the horizontal. Turning to Maple to avoid the ... other) software to plot the slope and deflection curves for the beams in Prob. 1, using the values (as needed) L =25in,a =15in,w =10lb/in,P = 150 lb. 3. Show that the shape factor for s...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21
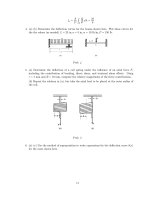
Introduction to Elasticity Part 8 pptx
... 0.2548E-10 -0. 2150 E -15 0.3253D-18 -0.7218D-10 -0.1228D -15 -0.1639E-16 -0. 2150 E -15 0.2083E-09 -0.6022D-16 -0.1228D -15 0.2228D-19 0.7218E-10 0.1084E-18 -0.6022E-16 0.3058D-09 -0.4265D-11 -0.1967D -15 0.6214E-22 ... Axes It is important to be able to transform the axes to and from the “laboratory” x − y frame to a natural material frame in which the axes might be labeled 1 −...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21

Introduction to Elasticity Part 9 pptx
... the stress intensity factor, with units of Nm −3/2 or psi √ in. (The factor π seems redundant here since it appears to the same power in both the numerator and denominator, but it is usually included ... be extremely difficult to fit solutions of the governing equations to them. One approach to this impasse is the experimental one, in which we seek to construct a physical laboratory mo...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 09:21