Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed - M Ashby D Jones (1999) WW Part 12 ppsx

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 12 ppsx
... more demanding struc- tural applications, have design methods evolved. In designing with ductile materials, a safety-factor approach is used. Metals can be used under static loads within a small ... pin of a pin-jointed frame, made of metal, fits poorly, then the metal deforms locally, and the pin beds down, redistribut- ing the load. But if the pin and frame are made of a brittle material, ....
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 3 ppsx
... metre of deformed metal is about 2 MJ, equiva-lent to 15 J mol −1 . When cold worked metals are heated to about 0.6T m , new strain-free grains nucleate and grow to consume all the cold-worked ... good example to begin with is solidification – most metals are melted or solidi ed during manufacture, and we have already looked at two case studies involving solidi- fication (zone refining, and ....
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 8 ppsx
... dried and fired, one com- ponent in it melts and spreads round the other components, bonding them together. Low-grade ceramics – stone, and certain refractories – are simply mined and shaped. We are ... metal such as molybdenum (usually applied as a powder and then heated). 200 Engineering Materials 2 Fig. 19.9. Forming methods for glass: pressing, rolling, float-moulding and blow-moulding....
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 9 ppsx
... necessitates a different design approach (Chapter 27). Most polymers are made from oil; the technology needed to make them from coal is still poorly developed. But one should not assume that dependence ... this chapter we examine three cement pastes: the primitive pozzolana; the widespread Portland cement; and the newer, and somewhat discredited, high-alumina cement. And we con- sider the pro...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures_ processing_ design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) WW Part 14 ppsx
... (a) Tin-rich solid plus lead-rich solid. (b) Liquid plus tin-rich solid. (c) Lead-rich solid only. (d) Liquid only. 2.6 (a) Liquid plus lead-rich solid between 1 and 2. (b) Lead-rich solid between ... When the temperature or pressure is decreased very rapidly, high temperature or high pressure phases can be “trapped”, and are observed at atmospheric temper- ature and pressure (diamond, for i...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:22

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 2 potx
... worked or heat-treated into finished products; and by understanding these, shape and size can, to a large extent, be predicted. Background reading M. F. Ashby and D. R. H. Jones, Engineering Materials ... what moving the molten zone along the bar has done to it: we have removed impurity from the left-hand end of the bar and dumped it at the right- hand end; that is, we have zone refine...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20
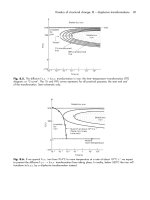
Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 4 pps
... devel- oped for use in the aerospace industry, they are now much more widely used. The dominant use of aluminium alloys is in building and construction: panels, roofs, and frames. The second-largest ... equilibrium temperature. If, instead of using undersaturated ammonium chloride solution, we pour saturated solution into the mould, we get what is called “big-bang” nucleation. As the freshly...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20

Engineering Materials Vol II (microstructures processing design) 2nd ed. - M. Ashby_ D. Jones (1999) Episode 5 pps
... wear and tear. Untempered martensite is far too brittle for hammer heads. Having solved the immediate problem to our satisfaction we still wondered how the manufacturer had managed to harden the ... bath of molten salt at 450°C. Finally, the heads are removed from the tempering bath and washed in cold water. The rather complicated austenitising treatment is needed be- cause the Standard insis...
Ngày tải lên: 13/08/2014, 05:20