david roylance mechanics of materials Part 4 pot

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 4 pot
... Advanced Strength of Materials, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1952 12 The Kinematic Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, ... mathematician Simeon Denis Poisson, (1781–1 840 ). 6 SHEAR AND TORSION David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technolo...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 9 pot
... Node # DOF 1 DOF 2 DOF 3 DOF 4 DOF 5 DOF 6 1 000000 2 0.013333 -0.03219 0000 3 0.02 -0.0 843 79 0000 4 000000 5 -0.0066667 -0.038856 0000 Element Stresses 1: 40 00 2: 2000 3: -2828 .4 4: 2000 5: ... = k (1) 11 k (1) 12 k (1) 13 k (1) 14 00 k (1) 21 k (1) 22 k (1) 23 k (1) 24 00 k (1) 31 k (1) 32 k (1) 33 + k (2) 11 k (1) 34 + k (2) 12 k (2) 13 k (2) 14 k...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 1 docx
... result can also be written 7 ATOMISTIC BASIS OF ELASTICITY David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 January 27, ... Newtons. Also using A = πd 2 /4 to compute the diameter rather than the area, we have d = 4A π = 4P f πσ f = 4 × 10000(lb) π × 600 × 10 6 (N/m 2 ) × 1 .44 9 × 10 4 lb/in 2...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 2 pdf
... 22–33 aramid 1 24 3.6 2.3 1 .45 86 2.5 22–33 boron 40 0 3.5 1.0 2 .45 163 1 .43 330 44 0 HS graphite 253 4. 5 1.1 1.80 140 2.5 66–110 HM graphite 520 2 .4 0.6 1.85 281 1.3 220–660 Of course, these materials ... neck. 5 INTRODUCTION TO COMPOSITE MATERIALS David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 5 ppt
... + ∂u ∂y dy 13 Transformation of Stresses and Strains David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 May 14, 2001 Introduction One of the most ... RAR −1 x y γ xy 3 The Equilibrium Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institut...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 6 ppt
... 0 000.0289 e ij = Σ ij 2G = 00.0378 0. 044 1 0.0378 0.0189 0.0567 0. 044 1 0.0567 −0.0189 The total strain is then ij = 1 3 kk δ ij + e ij = 0.00960 0.0378 0. 044 1 0.0378 0.0285 0.0567 0. 044 1 0.0567 −0.00930 If ... to 1. 2 Constitutive Equations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21
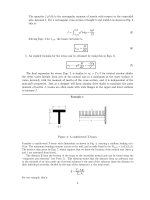
david roylance mechanics of materials Part 7 ppsx
... variation of stress as a function of height in a beam of irregular cross section. Another common design or analysis problem is that of the variation of stress not only as a function of height ... Strain, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989. 9 Beam Displacements David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0213...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 8 doc
... matrix: 0.1185E+12 0.1653E+10 0.2 942 E+ 04 -0.2798D+11 0.0000D+00 0.7354D+03 0.1653E+10 0.1185E+12 0.1389E+06 0.0000D+00 0.2798D+11 0. 347 3D+05 0.2 942 E+ 04 0.1389E+06 0 .48 00E+10 0.7354D+03 0. 347 3D+05 0.0000D+00 -0.2798E+11 ... − a 2 r 2 + σ 2 1+ 3a 4 r 4 − 4a 2 r 2 cos 2θ σ θ = σ 2 1+ a 2 r 2 − σ 2 1+ 3a 4 r 4 cos 2θ (19) τ rθ = − σ 2 1 − 3a 4 r 4 + 2a 2...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 10 ppt
... x=1.19 644 y=-0 z=0 3 x=0.9 845 62 y=0.167939 z=0 constraint=free 4 x=0. 940 6 34 y=0.335 841 z=0 5 x=1.07888 y=0.235833 z=0 . . . 72 x=3.99602 y=3.01892 z=0 73 x=3.99602 y=3.51 942 z=0 74 x=3.33267 y =4 z=0 75 ... (3,1) 13 ENGINEERING VISCOELASTICITY David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Octobe...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21

david roylance mechanics of materials Part 11 ppsx
... Plastic Flow David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 October 15, 2001 Introduction In our overview of the tensile ... 0 ◦ C for the polyurethane of Prob. 18 gives the following values of E rel (t)atvarioustimes: log(t, min) E rel (t), psi -6 56,280 -5 22,880 -4 4 ,45 0 -3 957 -2 578 -1 48 1 0...
Ngày tải lên: 11/08/2014, 02:21