Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J Lumelsky Part 11 docx

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 11 docx
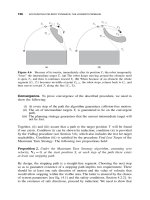
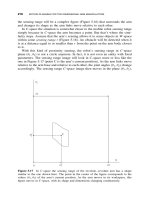
... types of elemental motions that appear in C, called Motion I, Motion II, Motion III, Motion IV, and Motion V, each corresponding to the P c (C-point) motion either along the P c (M-line) or along ... ·m > 0 and downward if b · m ≤ 0. 2. The C-point moves along the M-line or along an intersection curve between the V-plane and an obstacle, and it is about to leave V-plane at the...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
... 181 q 1 q 2 q 1 q 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 2 J o J o J o J o J o J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 q 2 l 1 l 2 a b (a)(b)(c) ( d )( e ) Figure 5.1 Five kinematically distinct two-link planar robot arms manipulators: ... utilization, overall investment, and engineering complexity Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
... obstacle; in Figure 5.23 these are lines 3-2 -1 and 5-6 -7 . • The straight-line segment that is a part of the W -space boundary; in Fig- ure 5.23, this is line 7-1 . Of these, the first three segments ... l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 < l 1 y x z Figure 5.21 The RR arm of Figure 5.19c. (a) The arm design. (b) Two projections of the arm W-space in case l 2 >l 1 . (c) Two projections of t...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 13 docx
... only the left-to-right (LtoR) data sets. The results are shown in Table 7.6. Given the significance level p<0.01, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that in the left-to-right task there ... 0. Let Q i , i = 1, ,m,andR j ,j = 1, ,n, be the ranks of X i and Y j ,respec- tively, among the N = (m + n) combined X and Y observations. That is, R j is the rank of Y j among the mXsa...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 14 docx
... [106, 134] and at the University of Wisconsin—Madison Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 389 RESULTS— EXPERIMENT TWO 373 Multivariate ... another group. Suppose µ ij represents the mean of the dependent variable i for group j , i = 1, 2, j = 1, 2. The mean vector for group j can be written as µ j = µ 1j µ 2...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... SENSING, INTELLIGENCE, MOTION HOW ROBOTS AND HUMANS MOVE IN AN UNSTRUCTURED WORLD Vladimir J. Lumelsky A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION ACKNOWLEDGMENTS When ... the field, a smooth motion and a less-than- wooden personality are not among them. A robotics Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... control • Compliant motion • Trajectory modification • Motion planning and collision avoidance; navigation Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, ... approaches to the go-from-A-to-B problem into two complementary groups—(1) motion planning with complete information and (2) motion planning with incomplete information—is ti...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... this way. • Motion planning with incomplete information, also called sensor-based motion planning or on-line motion planning,orpath planning with uncer- tainty,ortheSensing Intelligence Motion (SIM) ... criterion, how does one judge the per- formance of a motion planning algorithm with uncertainty? Given the real-time nature of SIM algorithms, they are expected to allow reasonably...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 4 pptx
... line is finite, we have d(L j )>d(H j +1 ). This produces a chain of inequalities for all H and L points, d(H 1 )>d(L 1 )>d(H 2 )>d(L 2 )>d(H 3 )>d(L 3 )>··· (3.8) Therefore, ... information such as approximation of obstacles with Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 73 86 MOTION PLANNING FOR A MO...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 5 pptx
... (S, H j ) because otherwise at least a part of the straight-line seg- ment (L j −1 ,H j ) would be included inside the obstacle. This is impossible VISION AND MOTION PLANNING 119 (a)(b) S L j T Q X j T i C S T Q L j X j T i C Figure ... set of hit and leave points, H j and L j , along the M-line so as to form a sequence of segments |ST | > |H 1 T | > |L 1 T | >...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21