Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J Lumelsky Part 8 doc

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 8 doc
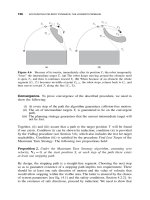
... does this all relate to the actual motion of the arm manipulator in W -space? The actual path in W-space whose reflection in C-space we just con- sidered is shown in Figure 5.14. The path created ... in W-space translates into a small displacement of the corresponding image point in C-space. A closed curve in W -space has its closed curve counterpart in C-space [105]. For an M-line in W -spa...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... SENSING, INTELLIGENCE, MOTION HOW ROBOTS AND HUMANS MOVE IN AN UNSTRUCTURED WORLD Vladimir J. Lumelsky A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION ACKNOWLEDGMENTS When ... the field, a smooth motion and a less-than- wooden personality are not among them. A robotics Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
... It INTRODUCTION 181 q 1 q 2 q 1 q 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 2 J o J o J o J o J o J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 q 2 l 1 l 2 a b (a)(b)(c) ( d )( e ) Figure 5.1 Five kinematically distinct two-link planar robot ... utilization, overall investment, and engineering complexity Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 177...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
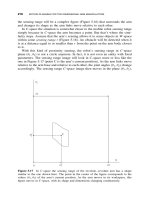
... obstacle; in Figure 5.23 these are lines 3-2 -1 and 5-6 -7 . • The straight-line segment that is a part of the W -space boundary; in Fig- ure 5.23, this is line 7-1 . Of these, the first three segments ... l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 < l 1 y x z Figure 5.21 The RR arm of Figure 5.19c. (a) The arm design. (b) Two projections of the arm W-space in case l 2 >l 1 . (c) Two projections of t...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 10 doc
... robot’s joint vector is j ∈ C. Similarly, L (j ) = n i L i (j ) ⊂ 3 is a set of points the whole robot occupies when its joint vector is j ∈ C. The workspace is defined as W = j ∈C L (j ) where L (j ... point: Condition 5 .8. 1. Let j ∗ ∈ C satisfy (5.7); that is, there exists u ∈ L such that w = u (j ∗ ) ∈ O. For given δ>0 and >0, define O = O ∩ U(w,δ), L = L ∩...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 11 docx
... types of elemental motions that appear in C, called Motion I, Motion II, Motion III, Motion IV, and Motion V, each corresponding to the P c (C-point) motion either along the P c (M-line) or along ... ·m > 0 and downward if b · m ≤ 0. 2. The C-point moves along the M-line or along an intersection curve between the V-plane and an obstacle, and it is about to leave V-plane at the...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 13 docx
... path Virtual–visible–LtoR 24 58. 77 18. 26 147.23 31.74 Virtual–visible–RtoL 24 176.92 29.54 391.41 91. 28 Virtual–invisible–LtoR 24 85 .82 21 .88 340.15 71.65 Virtual–invisible–RtoL 24 156. 08 17.59 392.41 96 .89 Physical–visible–LtoR ... only the left-to-right (LtoR) data sets. The results are shown in Table 7.6. Given the significance level p<0.01, we reject the null hypothesis and c...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 14 docx
... Effect Error Error F-Value p-Level 1 1 5 283 .137 91 12592 .88 0.419534 0.5 188 01 2 1 77.399 91 12592 .88 0.006146 0.937 684 12 1 85 98. 556 91 12592 .88 0. 682 811 0.410 782 DISCUSSION 381 TABLE 7.20. Results ... Error Error F -Value p-Level 1 1 1339396.0 92 3 286 4 .84 40.75467 0.000000 2 1 210132.0 92 3 286 4 .84 6.39 382 0.013155 12 1 685 8.0 92 3 286 4 .84 0.2 086 7 0.6 488 86 Hence...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... control • Compliant motion • Trajectory modification • Motion planning and collision avoidance; navigation Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, ... approaches to the go-from-A-to-B problem into two complementary groups—(1) motion planning with complete information and (2) motion planning with incomplete information—is ti...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... this way. • Motion planning with incomplete information, also called sensor-based motion planning or on-line motion planning,orpath planning with uncer- tainty,ortheSensing Intelligence Motion (SIM) ... criterion, how does one judge the per- formance of a motion planning algorithm with uncertainty? Given the real-time nature of SIM algorithms, they are expected to allow reasonably...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21