Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J Lumelsky Part 7 docx
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
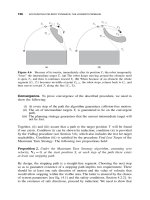
... 181 q 1 q 2 q 1 q 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 2 J o J o J o J o J o J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 q 2 l 1 l 2 a b (a)(b)(c) ( d )( e ) Figure 5.1 Five kinematically distinct two-link planar robot arms manipulators: ... overall investment, and engineering complexity Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 177 MINIMUM T...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
... obstacle; in Figure 5.23 these are lines 3-2 -1 and 5-6 -7 . • The straight-line segment that is a part of the W -space boundary; in Fig- ure 5.23, this is line 7- 1 . Of these, the first three segments ... M-lines shown. (The sketches are not to the same scale.) 242 MOTION PLANNING FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL ARM MANIPULATORS 0 5 4 2 2 5 A A B 6 3 2,3,5, 6 1 1 3 7 8 9 S,1,4,9 7 8 9 6 B...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 11 docx
... types of elemental motions that appear in C, called Motion I, Motion II, Motion III, Motion IV, and Motion V, each corresponding to the P c (C-point) motion either along the P c (M-line) or along ... ARM 277 l 3 d e c b a P o l 3 J 3 l 2 l 1 l 1 J 2 J 1 l 2 O 1 O 2 O 3 g f l 3max l 2max l 1max Figure 6.2 The work space of a 3D Cartesian arm: l 1 , l 2 ,andl 3 are links; J...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 13 docx
... 392.41 96.89 Physical–visible–LtoR 23 27. 70 13.92 51.69 11.64 Physical–visible–RtoL 24 142. 97 15 .78 396.45 109.38 Physical–invisible–LtoR 24 60. 57 15. 17 306.13 75 .78 Physical–invisible–RtoL 23 160.19 ... a simple two-link revolute–revolute arm, shown in Figure 7. 5. As before, the subject is sitting in O 2 J 1 S T P Θ 2 O 3 O 4 O 1 J 0 Θ 1 l 1 l 2 Figure 7. 5 This simple plan...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 14 docx
... Error F -Value p-Level 1 1 13860.02 10 77 56.985 1 .78 678 0 0.210934 2 1 6281.40 10 72 92.9 07 0.861303 0. 375 232 12 1 1 270 6.58 10 72 92.9 07 1 .74 2321 0.216262 TABLE 7. 19. Results of ANOVA on Completion ... F -Value p-Level 1 1 5248143.0 184 51 978 .68 100.9 672 0.000000 2 1 18 971 9.0 184 51 978 .68 3.6499 0.0 576 26 3 1 3 475 104.0 184 51 978 .68 66.8563 0.000000 12 1 12523.0 1...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... SENSING, INTELLIGENCE, MOTION HOW ROBOTS AND HUMANS MOVE IN AN UNSTRUCTURED WORLD Vladimir J. Lumelsky A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION ACKNOWLEDGMENTS When ... the field, a smooth motion and a less-than- wooden personality are not among them. A robotics Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... control • Compliant motion • Trajectory modification • Motion planning and collision avoidance; navigation Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 27 KINEMATICS ... approaches to the go-from-A-to-B problem into two complementary groups—(1) motion planning with complete information and (2) motion planning with incompl...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... this way. • Motion planning with incomplete information, also called sensor-based motion planning or on-line motion planning,orpath planning with uncer- tainty,ortheSensing Intelligence Motion (SIM) ... time, was born on April 15, 170 7, in Basel, Switzerland, and spent most of his career, between 172 7 and 174 1 and then from 176 6 until his death on September 18, 178 3, in St. Peter...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 4 pptx
... information such as approximation of obstacles with Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 73 86 MOTION PLANNING FOR A MOBILE ROBOT If point ... line is finite, we have d(L j )>d(H j +1 ). This produces a chain of inequalities for all H and L points, d(H 1 )>d(L 1 )>d(H 2 )>d(L 2 )>d(H 3 )>d(L 3 )>...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 5 pptx
... (S, H j ) because otherwise at least a part of the straight-line seg- ment (L j −1 ,H j ) would be included inside the obstacle. This is impossible VISION AND MOTION PLANNING 119 (a)(b) S L j T Q X j T i C S T Q L j X j T i C Figure ... set of hit and leave points, H j and L j , along the M-line so as to form a sequence of segments |ST | > |H 1 T | > |L 1 T | >...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21