Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J Lumelsky Part 4 pptx

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 4 pptx
... line is finite, we have d(L j )>d(H j +1 ). This produces a chain of inequalities for all H and L points, d(H 1 )>d(L 1 )>d(H 2 )>d(L 2 )>d(H 3 )>d(L 3 )>··· (3.8) Therefore, ... information such as approximation of obstacles with Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 73 86 MOTION PLANNING FOR A MO...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 5 pptx
... (S, H j ) because otherwise at least a part of the straight-line seg- ment (L j −1 ,H j ) would be included inside the obstacle. This is impossible VISION AND MOTION PLANNING 119 (a)(b) S L j T Q X j T i C S T Q L j X j T i C Figure ... set of hit and leave points, H j and L j , along the M-line so as to form a sequence of segments |ST | > |H 1 T | > |L 1 T | >...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... Braking 148 4. 2 .4 Optimal Straight-Line Motion 149 4. 2.5 Dynamics and Collision Avoidance 152 4. 2.6 The Algorithm 1 54 4.2.7 Examples 157 4. 3 Minimum Time Strategy 159 4. 3.1 The Model 160 4. 3.2 Sketching ... Exercises 135 4 Accounting for Body Dynamics: The Jogger’s Problem 139 4. 1 Problem Statement 139 4. 2 Maximum Turn Strategy 144 4. 2.1 The Model 144 4. 2.2 Sketchi...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... control • Compliant motion • Trajectory modification • Motion planning and collision avoidance; navigation Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, ... approaches to the go-from-A-to-B problem into two complementary groups—(1) motion planning with complete information and (2) motion planning with incomplete information—is ti...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... = D 11 D 12 D 13 D 14 D 15 D 16 D 12 D 22 D 23 D 24 D 25 D 26 D 13 D 23 D 33 D 34 D 35 D 36 D 14 D 24 D 34 D 44 D 45 D 46 D 15 D 25 D 35 D 45 D 55 D 56 D 16 D 26 D 36 D 46 D 56 D 66 (2.15) The ... r 3 (2z 3 +r 3 )s 2 θ 2 +r 2 2 + m 4 1 2 k 2 41 1 s 2 θ 2 (2s 2 θ 4 −1) +s 2 θ 4 + 1 2 k 2 42 2 (1 +c 2 θ 2 +s 2 θ 4 ) + 1...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 6 pot
... holonomic and, second, Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 139 PROBLEM STATEMENT 141 jogger’s mass and speed to the visible field ... information (Piano Mover’s model) and motion planning with incomplete information [other names are sensor-based planning, or Sens- ing Intelligence Motion (SIM)]. The idea is to use sens...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
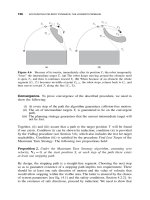
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
... 181 q 1 q 2 q 1 q 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 2 J o J o J o J o J o J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 q 2 l 1 l 2 a b (a)(b)(c) ( d )( e ) Figure 5.1 Five kinematically distinct two-link planar robot arms manipulators: ... utilization, overall investment, and engineering complexity Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 8 doc
... MANIPULATORS B A A B T S P 2 a 13 a 14 a 1 a 2 a 3 a 5 a 6 a 8 a 9 a 7 O P 1 a 4 b 7 b 2 b 3 b 4 b 5 b 6 a 10 a 11 a 12 b 8 b 9 b 10 b 11 b 12 b 13 b 14 b T a' T a T '' b' b'' b 1 Figure 5.3 Obstacles A and ... all relate to the actual motion of the arm manipulator in W -space? The actual path in W-space whose reflection in C-space we just con- sidered i...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
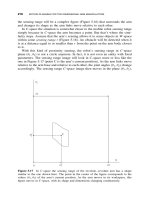
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
... obstacle; in Figure 5.23 these are lines 3-2 -1 and 5-6 -7 . • The straight-line segment that is a part of the W -space boundary; in Fig- ure 5.23, this is line 7-1 . Of these, the first three segments ... l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 < l 1 y x z Figure 5.21 The RR arm of Figure 5.19c. (a) The arm design. (b) Two projections of the arm W-space in case l 2 >l 1 . (c) Two projections of t...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 10 doc
... robot’s joint vector is j ∈ C. Similarly, L (j ) = n i L i (j ) ⊂ 3 is a set of points the whole robot occupies when its joint vector is j ∈ C. The workspace is defined as W = j ∈C L (j ) where L (j ... 5.8.1. Let j ∗ ∈ C satisfy (5.7); that is, there exists u ∈ L such that w = u (j ∗ ) ∈ O. For given δ>0 and >0, define O = O ∩ U(w,δ), L = L ∩ U(u,δ), and O C =...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21