Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 2 ppsx
... Cartesian coordinates: Position: cos θ 2 = x 2 + y 2 − l 2 1 − l 2 2 2l 1 l 2 θ 1 = tan −1 y x − tan −1 l 2 sin θ 2 l 1 + l 2 cos θ 2 (2. 5) Velocity: ˙ θ 1 ˙ θ 2 = 1 l 1 l 2 sin θ 2 l 2 cos(θ 1 + θ 2 )l 2 sin(θ 1 + θ 2 ) −l 1 cos ... = ˙x ˙y = −l 1 sin θ 1 − l 2 sin(θ 1 + θ 2 ) − l 2 sin(θ 1 + θ 2 ) l 1 cos θ 1 + l 2 cos(θ 1 + θ 2 )l...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 1 doc
... Programming 21 1 .2. 7 Motion Planning 24 2 A Quick Sketch of Major Issues in Robotics 27 2. 1 Kinematics 29 2. 2 Statics 33 2. 3 Dynamics 33 2. 4 Feedback Control 37 2. 5 Compliant Motion 40 2. 6 Trajectory Modification ... 183 5 .2 Planar Revolute–Revolute (RR) Arm 187 5 .2. 1 Analysis 189 5 .2. 2 Algorithm 21 0 5 .2. 3 Step Planning 21 1 5 .2. 4 Example 21 2 5 .2. 5 Mo...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 3 pot
... m 1 k 2 122 + m 2 k 2 211 s 2 θ 2 + k 2 233 c 2 θ 2 + r 2 (2y 2 + r 2 ) + m 3 k 2 322 s 2 θ 2 + k 2 333 c 2 θ 2 + r 3 (2z 3 +r 3 )s 2 θ 2 +r 2 2 + m 4 1 2 k 2 411 s 2 θ 2 (2s 2 θ 4 −1) ... +s 2 θ 4 + 1 2 k 2 422 (1 +c 2 θ 2 +s 2 θ 4 ) + 1 2 k 2 433 s 2 θ 2 (1 −2s 2 θ 4 ) − s 2 θ 4 + r 2 3 s 2 θ...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 4 pptx
... [0, 2 ], l 2 = [l 2min , l 2max ]; ranges of both joints, respectively: l 2 = (l 2max − l 2min ); l 1 = const > 0 − lengths of links. l 1 J o J 1 q 1 l 2 Figure 2. E.1 2. Design a straight-line ... line is finite, we have d(L j )>d(H j +1 ). This produces a chain of inequalities for all H and L points, d(H 1 )>d(L 1 )>d(H 2 )>d(L 2 )>d(H 3 )>d(L 3 )>...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 5 pptx
... algorithm VisBug -2 1 performs better (Figure 3.15) than algorithm VisBug -2 2 (Figure 3 .21 ), but luck switches to VisBug -2 2 in another scene shown in Figure 3 .23 . Convergence of algorithm VisBug -2 2 follows ... called VisBug -2 2 , is also tied to the mechanism of Bug2 procedure, but more loosely. The algorithm behaves more opportunisti- cally compared to VisBug -2 1 . Instead of the...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 6 pot
... cos θ(t) − 2p sin θ(t) 4p 2 + q 2 V 2 (t) + B (4.7) where terms A and B are A = x 0 − V 0 2 (2p cos(θ 0 ) + q sin(θ 0 )) 4p 2 + q 2 B = y 0 + V 0 2 (q cos(θ 0 ) − 2p sin(θ 0 )) 4p 2 + q 2 Equations ... holonomic and, second, Sensing, Intelligence, Motion, by Vladimir J. Lumelsky Copyright 20 06 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 139 PROBLEM STATEMENT 141 jogger’s mass an...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 7 docx
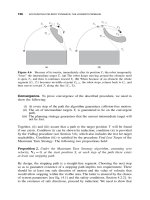
... It INTRODUCTION 181 q 1 q 2 q 1 q 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 1 l 2 J o J o J o J o J o J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 J 1 q 2 l 1 l 2 a b (a)(b)(c) ( d )( e ) Figure 5.1 Five kinematically distinct two-link planar robot ... θ(t) − 2p sin θ(t) 4p 2 + q 2 V 2 (t) + B (4.15) where terms A and B are A = x 0 − V 0 2 ( 2 p cos(θ 0 ) +q sin(θ 0 ) ) 4 p 2 + q 2 B = y 0 + V 0...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 8 doc
... θ S 1 M 2 : p = θ T 2 − θ S 2 − 2 ·δ 2 θ T 1 − θ S 1 ,q= θ T 1 · θ S 2 − θ T 2 · θ S 1 + 2 ·δ 2 · θ S 1 θ T 1 − θ S 1 M 3 : p = θ T 2 − θ S 2 θ T 1 − θ S 1 − 2 ·δ 1 ,q= θ T 1 · θ S 2 − θ T 2 · ... θ S 1 − 2 ·δ 1 · θ S 2 θ T 1 − θ S 1 − 2 · δ 1 M 4 : p = θ T 2 − θ S 2 − 2 ·δ 2 θ T 1 − θ S 1 − 2 ·δ 1 ,q= θ T 1 · θ S 2 − θ T 2 · θ S 1 − 2 ·(δ 1 · θ S 2...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21
Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 9 docx
... 22 1 x 2 y o J 1 x o z o (a)(b) (c)(d) J 1 J 2 z o x o x 1 x 2 a 2 J 2 z 2 a 1 x o x 1 z o y o z 1 x 1 q 1 q 2 J 1 x 2 z 1 z 2 q 1 q 2 y o P P a 1 a 2 l 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 y 1 x 1 l 2 l 1 z 1 a 2 J 2 x 2 x 1 y o J 1 x 1 x o x 2 z o P z 1 J 2 l 2 l 1 q 2 q 2 q 1 q 1 P Figure ... 11,15 16 13,16 M 1 M 2 17 0 17 ,22 18 18 ,20 19 C 19 20...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21

Sensing Intelligence Motion - How Robots & Humans Move - Vladimir J. Lumelsky Part 10 doc
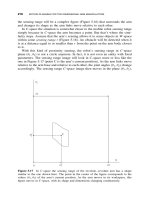
... 2- chain C 2 0 on G 0 such that 1 0 = ∂C 2 0 ; and, if C 2 1 is the subdivided form of C 2 0 on G 1 ,then∂C 2 1 = 1 + ∂C 2 . Hence by Theorem 5.9 .2 ∂(C 2 1 + C 2 2 ) = ( 1 + ∂C 2 ) + ∂C 2 = ... solution to the motion planning task. 26 0 MOTION PLANNING FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL ARM MANIPULATORS a 2 a 1 a * B b * b 1 b 2 A a * a * b 1 B a 2 ′′ b 2 ′′ a 2 ′′...
Ngày tải lên: 10/08/2014, 02:21