Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 2 pptx

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 2 pptx
... respectively, r (a) 2 (s g ,θ g ) = M 2g r (a) g (s g ,θ g ) (21 .3. 22 ) r (b) 2 (λ w ,θ g ) = M 2g r (b) g (λ w ,θ g ). (21 .3. 23 ) Here, M 2g = M 2a 2 M a 2 m 2 M m 2 g (21 .3. 24 ) where M m 2 g = 100 ... R u ± P w 2 /2) R g (Fig. 21 .3. 3) Radial setting S r 2 (Fig. 21 .3. 2) Basic cradle angle q 2 (Fig. 21 .3. 2) Machine center to back ...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 4 pptx
... γ 2 (22 .3. 19) y (P) f = r 2 tan γ 2 − E sin γ 2 cos 2 γ 1 − sin 2 γ 2 (22 .3. 20 ) z (P) f = r 2 sin γ 1 cos γ 2 (22 .3. 21 ) n (P) xf = cos 2 γ 2 − sin 2 γ 1 (22 .3. 22 ) n (P) yf =−sin γ 2 (22 .3. 23 ) n (P) zf =−sin ... γ 1 ] T (22 .4 .2) τ (2) = O 2 P |O 2 P | = ∂r (2) f ∂u 2 ∂r (2) f ∂u 2 = [sin γ 2 cos θ 2 − co...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 7 pptx
... 27 .3. 3 yields r (1) 2 + λ 1 a (1) 2 = r (2) 2 + λ 2 a (2) 2 + C (27 .3. 19) where λ 1 a (1) 2 = MA,λ 2 a (2) 2 = NB. Then, we obtain r (1) 2 − r (2) 2 = C +λ 2 a (2) 2 − λ 1 a (1) 2 . (27 .3. 20 ) We ... (27 .3. 20 ) by the unit vector c 2 = a (1) 2 × a (2) 2 a (1) 2 × a (2) 2 and take into account that C · c 2 = C, a (1) 2 · a (...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21
Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 1 potx
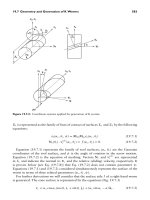
... (Figs. 19. 12. 1 and 19. 12. 2). Figure 19. 12. 2: Intersection of worm and worm- gear surfaces by plane m−n. P1: JsY CB6 72- 19 CB6 72/ Litvin CB6 72/ Litvin-v2.cls February 27 , 20 04 1 :28 594 Worm -Gear Drives ... JsY CB6 72- 19 CB6 72/ Litvin CB6 72/ Litvin-v2.cls February 27 , 20 04 1 :28 19.7 Geometry and Generation of K Worms 587 The final expressions for both sides of...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 3 ppsx
... are applied: tan 2 (1p) = −2d 13 d 23 d 2 23 − d 2 13 − (k f − k h )d 33 k t − k p = −2d 13 d 23 d 33 sin 2 (1p) k t + k p = k f + k h + d 2 13 + d 2 23 d 33 . (21 .5 .28 ) Equation (21 .5 .24 ) ... follows: tan 2 (g2) = −2c 13 c 23 c 2 23 − c 2 13 − (k g − k u )c 33 k q − k s = −2c 13 c 23 c 33 sin 2 (g2) k q + k s = k g + k u + c...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 5 ppt
... addition to Eqs. ( 23 . 3.1) to ( 23 . 3 .3) , we use equation N 2 = N 3 − N 1 2 ( 23 . 3.4) obtained from Fig. 23 . 2. 4, and the equation [see Eq. ( 23 . 2. 12) ] ω c ω 1 = N 1 N 1 + N 3 = m (3) c1 . ( 23 . 3.5) Using ... ω c ). ( 23 . 5.5) Equations ( 23 . 5 .3) , ( 23 . 5.4), and ( 23 . 5.5) yield η (3) 1c = 1 − ψ (c) N 3 N 1 + N 3 . ( 23 . 5.6) P1: JXR CB6 72- 2...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 6 pps
... (Fig. 25 .1.1), and y 1 (u c ,θ c ,ψ) + z 1 (u c ,θ c ,ψ) tan λ p = 0. (25 .3. 3) Equations (25 .3. 1) and (25 .3. 3) yield F (u c ,θ c ,ψ) = 0. (25 .3. 4) The system of Eqs. (25 .3. 2) and (25 .3. 4) represents ... t and g ). P1: GDZ/SPH P2: JXR CB6 72- 26 CB6 72/ Litvin CB6 72/ Litvin-v2.cls February 27 , 20 04 2 :33 7 52 Generation of Surfaces by CNC Machines Step 2: D...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 3 Part 8 docx
... 38 , 45, 49, 50, 115, 137 , 21 1, 27 4, 28 0, 28 8, 28 9, 29 6, 29 8, 35 2 noncircular gears, of, 31 8, 32 2 33 4, 33 7, 33 8, 34 1, 34 3 34 6, 34 8, 34 9, 35 5, 35 6, 35 9, 36 0 Circular pitch, 39 0 Clearance, 609 Computer ... 99, 37 5, 38 3, 39 2, 39 5 Instantaneous center of rotation, 37 , 44, 45, 48, 101, 120 , 121 , 137 , 138 , 144, 27 1, 27 2, 27 4, 27...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21

Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 1 Part 9 pot
... equations cos 2 (1) = g 1 − g 2 cos 2 ( 12) g 2 1 − 2g 1 g 2 cos 2 ( 12) + g 2 2 1 /2 (9 .3. 21 ) sin 2 (1) = g 2 sin 2 ( 12) g 2 1 − 2g 1 g 2 cos 2 ( 12) + g 2 2 1 /2 . (9 .3. 22 ) The minor axis 2b ... κ q )a 33 (8.4.49) κ f − κ h = 2a 13 a 23 a 33 sin 2 = a 2 23 − a 2 13 + (κ s − κ q )a 33 a 33 cos 2 (8.4.50) κ f + κ h = (...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21
Gear Geometry and Applied Theory Episode 1 Part 10 pps
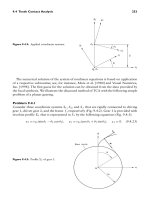
... 2 of gear 2. Gear 2 is provided with involute profile 2 that is represented in S 2 by the equations (Fig. 9.4.4) x 2 = r b2 (−sinθ 2 + θ 2 cos θ 2 ), y 2 = r b2 (−cosθ 2 − θ 2 sin θ 2 ), z 2 = ... φ 1 ) ] −r b2 [ −sin(θ 2 + φ 2 ) + θ 2 cos(θ 2 + φ 2 ) ] = 0 (9.4 . 32 ) r b1 [ cos(θ 1 − φ 1 ) + θ 1 sin(θ 1 − φ 1 ) ] −r b2 [ −cos(θ 2 + φ 2 ) − θ...
Ngày tải lên: 08/08/2014, 12:21