Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 11 ppt

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 11 ppt
... control (grooved-rake tool) 25 1 2 high manganese steel machining 21 5–17 machining a-brass 20 6–7 three-dimensional chip flow 20 9, 25 5– 62 Iterative convergence method (principles) 20 5–7, 21 2–15 Jobbing ... [W/mK] P01–10 50 16 20 6 8 < 2 6900 16 .2 1 .2 20 P05 25 49 16 15 8 12 < 2 7000 14 .2 1.8 20 P01–15 48 16 20 5 11 –* 7000 15.7 –* 20 P05 Total carbi...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 8 pptx
... 3(s xx ′ 2 + s yy ′ 2 + s zz ′ 2 ) + 6(s 2 xy + s 2 yz + s 2 zy ) ≡ (s xx – s yy ) 2 + (s yy – s zz ) 2 + (s zz – s xx ) 2 + 6(s 2 xy + s 2 yz + s 2 zy ) = 6k 2 or 2Y 2 (A1 .26 b) which is the same ... s r 2 . So s r is also a stress invariant (it is known as the second stress invariant). From equation (A1 .25 ) s r 2 = s 2 xx + s 2 yy + s 2 zz +2( s 2...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 7 ppt
... addition s r ′ 2 = s r 2 –3s m 2 =(s 1 2 + s 2 2 + s 3 2 ) – 3s m 2 (A1.5) After substituting for s m from equation (A1.1), 3s r ′ 2 =(s 1 – s 2 ) 2 +(s 2 – s 3 ) 2 +(s 3 – s 1 ) 2 (A1.6) The yield ... stresses: 1 s – 2 =— [ (s 1 – s 2 ) 2 +(s 2 – s 3 ) 2 +(s 3 – s 1 ) 2 ] = Y 2 or 3k 2 (A1.7) 2 330 Appendix 1 Fig. A1 .2 Geometrical representation...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 4 pptx
... conventional, (b) and (c) type I and II tools, K = 1 .2 Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 3:19 pm Page 26 2 where F* t , F* r and F* z are the specific cutting forces in the tangential, radial and axial direc- tions, ... analysis Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 3:18 pm Page 25 3 strain rate for the plane-faced tool and type I and II tools with K = 1 .2. The type I tool produces narr...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 10 pot
... stainless 21 24 22 25 23 26 24 27 25 29 austenitic stainless 14–17 15–18 17 21 22 25 26 29 high manganese 14 16 19 21 22 Aluminium pure, 1000 series 20 0 24 0 20 0 23 0 20 0 22 5 190 22 0 – 20 00 to 7000 ... copper* 115 – 120 100 110 90–100 – – 60/70Cu–40/30Zn 25 –35 28 –35 27 –33 25 –30 – 90/95Cu–10/5Sn 15 25 20 25 23 –30 – – 60/90Cu–40/10Ni 6–15 8–18 12 22 – – Nickel...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 9 doc
... u˘ z d l hD ikj 21 10 + —— [ 121 0 ] 12 1 120 0000 (A2 .26 ) and 11 1 q*V e 1 qD ikj 1 hT 0 D ikj 1 {F} e = ——— {} – ——— {} – ——— {} (A2 .27 ) 4 1 3 1 3 1 10 0 Global assembly of equations (A2 .20 a), with ... {F e } (A2.30) ∂t with rCV e 21 11 [C] e = ——— | 121 1 | 20 1 121 11 12 ([C] is given here for a four-node tetrahedron). Numerical (finite element) methods 361 Fig....
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 6 pot
... [mm] SVVBN2 525 M16 VBMM160404 53 P10 49 0.10 0.33 5 12 17 35 0.4 MVVNN2 020 M16 VNMG160404 53 P10 45 0 .20 0.48 4 11 17 35 0.4 MVVNN2 020 M16 VNMG160408 53 P10 38 0.40 0.70 4 11 17 35 0.8 Childs Part 3 ... (HALT)) 2: (TOOL reamer 20 .0) 3: (SHAPE through-hole 19.5 ∇) 2: (TOOL reamer 20 .0) 4: (TOOL drill 19.5) 5: (SHAPE through-hole 11. 7 ∇) 2: (TOOL reamer 20 .0) 4: (TOOL dril...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 5 ppsx
... d R ) 2 – (r w – d e ) 2 = R 2 – (R – d e ) 2 } (9.9a) for a convex survace (r w + d R ) 2 – (r w + d e ) 2 = R 2 – (R – d e ) 2 Hence d e 2r w – d R for a concave surface c r = — = ———— d R 2r w – ... (9 .26 a) (C11) R = Ȉȉȉȉȉȉ F 2 1 + F 2 2 + F 2 3 ȉ ≤ R max = min{R 1,max , , R i,max , . . .} (9 .26 b) where j = 1, 2, 3 represents the three orthogonal directions of f...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20
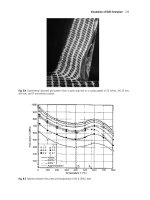
Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 3 pot
... –0.000015(T–370) 2 a = 0.00 028 , m = 0.0016 Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 3:17 pm Page 24 2 24 6 Applications of finite element analysis Fig. 8.16 continued Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 3:17 pm Page 24 6 Figure 8.16. ... –0.0005T + 0.1e –0.000015(T–430) 2 a = 0.00 020 , m = 0.00 52 Steel Y A = 920 e –0.0011T + 120 e –0.00003(T–160) 2 + 110 e –0.00004(T–340) 2 + 120 e –...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20

Metal Machining - Theory and Applications Episode 2 Part 2 pps
... (ICM) 21 3 Fig. 7. 12 Developed flow-chart of the iterative convergence method Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 3:15 pm Page 21 3 22 8 Applications of finite element analysis Fig. 8.1 continued Childs Part 2 28:3 :20 00 ... j–1 and j, and L j is the separation between nodes j–1 and j: ᐉ j = ( (u˘ x,j–1 + u˘ x,j ) 2 + (u˘ y,j–1 + u˘ y,j ) 2 ) 1 / 2 (7.11a) L j = ( (x j–1 –...
Ngày tải lên: 21/07/2014, 17:20
- uwb theory and applications
- the structure of complex networks theory and applications
- the marginal cost of public funds theory and applications
- theory and applications spread spectrum systems ppt
- the structure of complex networks theory and applications ernesto estrada
- the structure of complex networks theory and applications download
- the structure of complex networks theory and applications pdf
- optical code division multiple access communication networks theory and applications pdf