The Illustrated Network- P73 pot

The Illustrated Network- P73 pot
... (another private IP address space). The NAT router knows the real public address of the IBM server, of course. The NAT router returns this private address to the client, which uses it as the ... the outside world? In other words, what if there is another 10.100.100.0/24 address range on the “outside” that the local device using that private address space must com- municate...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 08:20

The Illustrated Network- P6 pot
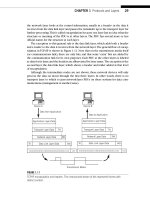
... (The numbers come from the ISO-RM.) As shown in the fi gure, there is a natural grouping of the fi ve-layer protocol stack at the network layer and the transport layer. The lower three layers ... protocols, but there are other proto- cols as well. The TCP/IP model is based on a fi ve-layer model for networking. From bottom (the link) to top (the user application), these are t...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20
The Illustrated Network- P7 potx
... of, the physical address used by the frames that carry the packets between adjacent systems. Why should the systems need two addresses for the two layers? Why can’t they just both use either the ... 3, which forwards the data, is the destination reachable.) These forwarding decisions are made at the TCP/IP network layer. The Network Layer The network layer delivers dat...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P18 pot
... this case, the IP address of the host is known (from the IP destination address on the packet) and the MAC address of the host must be found. Let’s look at Case 1 in detail because the others are ... address of a host on the same subnet as the source. Case 2: Find the address of a router on the same subnet as the source. Case 4: Find the address of a host on the s...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P20 potx
... point-to-point links), they came up with the term “datagram.” The IP layer of the whole TCP/IP protocol stack is the very heart of TCP/IP. The frames that are sent and delivered across the network from ... learn about the IP layer. We’ll start with the fi elds in the IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers. We’ll discuss most of the fi elds in detail and show how many of them relat...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P28 pot
... router and the TTL is not 1 or 0, then the router dec- rements the TTL fi eld and forwards the packet out the interface leading to the next hop on the way to the destination address. 3. If the packet ... memory, the shared DRAM handles the packet buffers in the router. Splitting the packet buffers from the other DRAM improves I/O performance, because the shared...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P31 potx
... numbers every time they are run. The server has no trouble replying to the proper client because the server can just reverse the source and destination port numbers to send a reply to the correct ... don’t want to add these to the application? Files cannot use quick request–response messages to transfer themselves over a network. That’s the job of TCP, which is the topic of...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P36 potx
... rules ϭ Gig Ethernet Note: All links use 10.0.x.y addressing only the last two octets are shown. FIGURE 13.1 The hosts on the LANs have routing tables as well as the routers. The ISPs on the Illustrated ... on the hosts on the LANs, as shown in Figure 13.1. But we’ll also discuss, for the fi rst time, how the two ISPs on the network (called Ace ISP and Best ISP) relat...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P38 potx
... such as the IXPs. This is one reason that Ace ISP and Best ISP in Figure 13.1 at the beginning of the chapter maintain multiple links between the four routers in the “quad” between their border ... collection of other ISPs just like Ace and Best. Can LAN1 reach LAN2 through the Internet”? Maybe. It all depends on the arrange- ments between our two ISPs and the ISPs at the...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 07:20

The Illustrated Network- P46 potx
... fxp0.0 disable; The local keyword means that the local router is the RP. The address is the RP address that will be used in PIM messages between the routers. The confi guration on the non-RP router, ... So, the source’s router (actually, the DR) encapsulates the multicast packets inside a unicast packet sent to the RP and tunnels the packet to the RP in this form...
Ngày tải lên: 04/07/2014, 08:20