Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 5 doc

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 4 docx
... “ishion” standing for hip, buttocks, sacrum, loin and also upper limb. Since the time of Hippocrates of Cos (46 0–370 B.C.), this term has relatedtopainsyndromeofthelowerbackandtheupperpartsofthelowerlimbs [57]. The ... (1930). 2 Section History of Spinal Disorders c d Figure 2. (Cont.) c Andreas Vesalius (15 14 15 64) . d Josias Weitbrecht’s (1702 – 1 747 ) Syndesmologia (1 742 ) p...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 5 doc
... [42]. Par ´e ( 151 0– 159 0) introduced a brace for scoliosis treatment A less cruel method of treating spinal deformities was developed by Ambroise Par´e ( 151 0– 159 0). The father of French surgery ... loca- tion and size of the lesion. There is often a history of trauma not immediately related to the present condition. Numbness and tingling, anaesthesia, partial or complet...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 6 docx
... of any major advancement in the treatment of spinal dis- orders. In the Renaissance, the studies of Andreas Vesalius (1514–1 564 ), the father of modern anatomy, led to a better understanding of ... dedicated to the research and treatment of spinal cord injuries ( Fig. 10c). He propagated intensive rehabilitation and sports. He also wrote a profound and epoch-making...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20
Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 17 docx
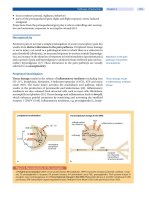
... the responsibleenzymefortetrahydrobiopterin(BH4)synthesis.BH4isanessential cofactor for catecholamine, serotonin and nitric oxide production and thus a key modulator of peripheral neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Healthy individu- Pathways of Spinal Pain ... integration and nociceptive transfer of noci- 144 Section Basic Science General Concepts of Pain Treatment Pharmac...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 23 docx
... work-up and initiation of treatment is mandatory. The major goal of the clinical assessment is to differentiate: specific spinal disorders, i.e. with a pathomorphological correlate non-specific spinal ... consider a spinal intervention ✔ The reproducibility of the patient’s history and examination is limited Epidemiology Generally, spinal pain is common, benign, and self...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 29 doc
... injection of 0.3 ml of contrast material. Anteroposterior spot radiographs are obtained for the documentation of the contrast material distribution. Two milliliters of 0.2% ropivacaine and 40 mg of triamcinolone ... value of discography because of a lack of understanding of pain pathogenesis [22–24, 78, 123]. Indications Inourservice,patientsareonlyselectedforprovocativedi...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 34 docx
... bilat- eral and complex symptoms (impaired upper limb – hand function, gait disorder, bladder and bowl dys- function). Duration of symptoms is important for the definition of etiology and urgency of therapy (e.g. ... (cave: spinal shock). Pathological reflexes indicate central (spinal and supraspinal) lesions. Motor strength is subdivided into six grades (M0–M5), and key mu...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 40 docx
... intubation degree of mouth opening size of the tongue visibility of the pharynx the state of dentition restriction of neck movement stability of the cervical spine Assessment of cervical stability is mandatory in ... preparation and to take into account those conditions which will add to the risk of anesthesia and surgery. Information and Instructions One aim of the pr...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20
Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 42 doc
... PGE 1 is capable of reducing MAP smoothly, maintaining the autoregulation of the spinal cord blood flow [79]. In spinal cord injury and compression, CHA can compromise remaining spinal cord function Caution ... taken to minimize compression and traction of linesand anatomic struc- tures. Cervical spine procedures call for a thorough final check of lines and tubes before pr...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 44 doc
... assessment of the different organ systems is self-evident ✔ Perioperative tachycardias are often combined with ischemic episodes, and their treatment is mandatory because of the high mortality of perioperative ... ileus, and nausea and delays mobilization and feeding. Effec- tive treatment of postoperative pain, therefore, results in modification of the biological respon...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 45 doc
... hypertrophy of the yellow ligament and causes a narrowing of the spinal canal and foramen. During later stages of segmental degeneration, kyphosis of the cervical spine can occur and further compromise ... irritation of the nerve roots and can lead to hyp- oxia of the nerve root and dorsal root ganglion. The subsequent release of proin- flammatory cytokines and NGF...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 49 doc
... comparison of cervical laminaplasty and cervical laminectomy with progressive facetectomy. Spine 18:1995–2004 190. Nurick S (1972) The natural history and the results of surgical treatment of the spinal ... operative treatment of 48 patients with mild and moderate forms of cervical spondylotic myelopa- thy (CSM). The authors concluded that surgical treatment of mild...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20
Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 54 doc
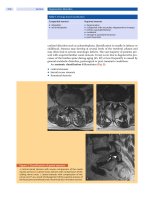
... course of spinal stenosis is generally benign Little is known about the natural history of spinal stenosis. Some authors reported that the natural course is benign and that the subjective and physical manifestations ... the type of stenosis (i.e. central, lateral recess, or foraminal) and the presence of concomitant back pain. The principal surgical options for decompression...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20
Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 55 doc
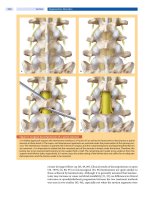
... spine, with and without spinal fusion, for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis without instability in 45 patients. The patients were randomly assigned to one of three treatment groups: Group ... decompression with laminotomy and medial facetectomy; Group II, with decompression and arthrodesis of the most stenotic segment; and Group III, with decompression and spin...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20

Spinal Disorders: Fundamentals of Diagnosis and Treatment Part 56 doc
... features,i.e.completelossofarticularcartilage, cysts and pseudocysts in the bone, dense bone sclerosis, and large osteophyte formation. Of note, spontaneous fusion of the facet joints is very rare in the absence of ... true incidence of symptomatic alterations of the motion segment. The natural history of LBP is benign The natural history of LBP related to degenerative lumba...
Ngày tải lên: 02/07/2014, 06:20
- diagnosis and treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults
- diagnosis and treatment of venous eczema
- fundamentals of electrical and electronic circuits
- current medical diagnosis and treatment 2009
- fundamentals of oop and data structures in java pdf download
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder adhd adults diagnosis and treatment guideline